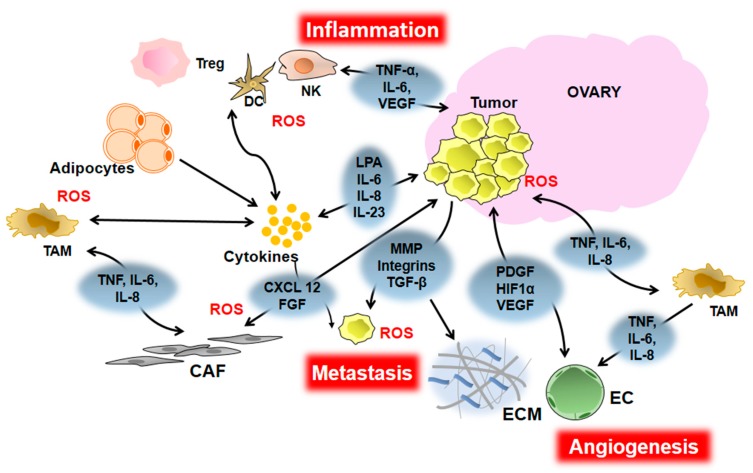
Figure 2.
Inflammatory mediators contributing to EOC progression, metastasis, and angiogenesis. EOC cells produce ROS, chemokines, cytokines, and growth factors that can: (1) Lead to recruitment of immune cells like Dentric cells (DC), Natural killer cells (NK), Tumor associated macrophages (TAMs), and T-regulatory (Treg) cells into the TME, which generate additional cytokines, ROS, and growth factors, resulting in chronic inflammation. (2) Stimulate the tumor cells themselves, the TAMs, and the surrounding fibroblasts (also known as cancer associated fibroblasts or CAFs) to proliferate and secrete growth factors like TGF-β and FGF that stimulate production of integrins and Matrix Metalloproteins (MMPs), resulting in migration of the tumor cell via degradation of the extra cellular matrix (ECM). (3) Stimulate endothelial cells (EC) to produce growth factors like PDGF and EGF and factors like VEGF that stimulate angiogenesis. The double arrows indicate that the cells are a source of the factor as well as stimulated by it.