Figure 3.
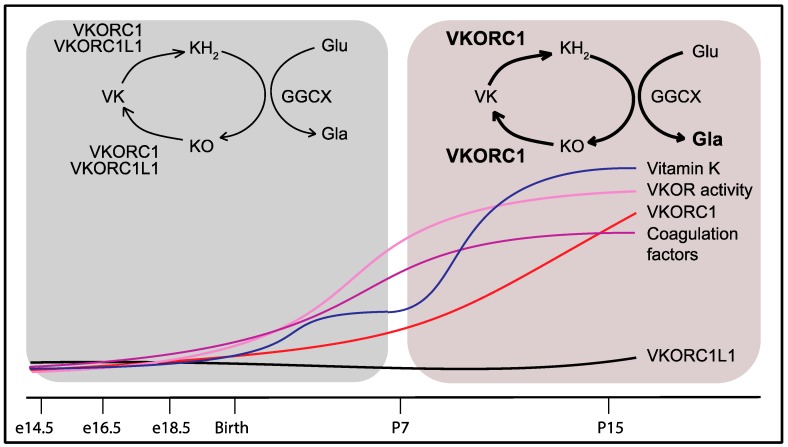
Developmental regulation of VKORC1 and of the vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors in the liver explains the partial redundancy of VKORC1L1. Around birth, VKORC1 and VKORC1L1 both support γ-carboxylation and hemostasis. Beyond P7, VKORC1 expression and activity increase in the liver with the level of vitamin K concomitantly rising in the bloodstream to handle the growing demand for coagulation factor γ-carboxylation. The lower expression levels of VKORC1L1 in the liver after P7 can no longer compensate for the absence of VKORC1 activity. VKORC1: Vitamin K oxidoreductase; VKORC1L1: VKORC1-like 1; VK: Vitamin K; KH2: Vitamin K hydroquinone; KO: Vitamin K 2,3-epoxide; GGCX: γ-glutamyl carboxylase; Glu: Glutamic acid residue; Gla: γ-carboxyglutamic acid residue.