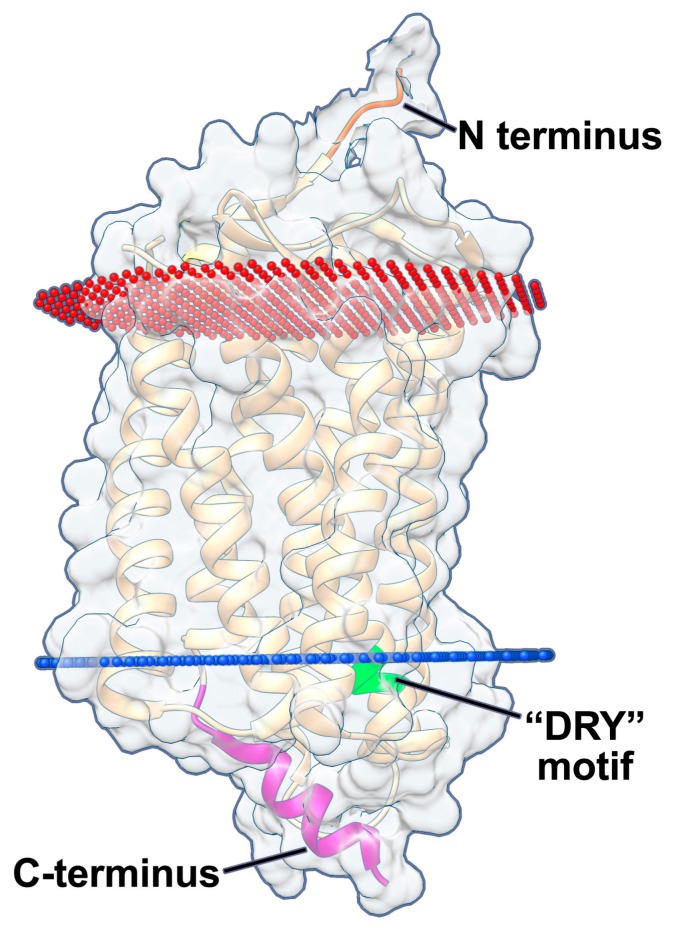
Figure 1.
HCMV pUS28 structure. The viral GPCR, pUS28 contains seven transmembrane spanning helices (beige). The N-terminus (orange) of the protein is extracellular and required for ligand binding, while the C-terminal domain (purple) is intracellular and important for protein trafficking. The Y16F ligand binding domain mutant is a single amino acid point mutation at position 16 found within the N-terminus (orange). The canonical “DRY” motif (green) is located within the second intracellular loop and is required for G-protein coupling. The R129A and R129Q mutants discussed herein mutate the arginine (R) of the “DRY” motif to an alanine (A) or glutamine (Q), which ablates G-protein coupling. Extracellular membrane, red; intracellular membrane, blue. The structure is based on the pUS28 crystal structure, bound to CX3CL1 ([34]; PDB ID: 4XT3), using Chimera [35] and the Orientations of Proteins in Membranes (OPM) databases [36].