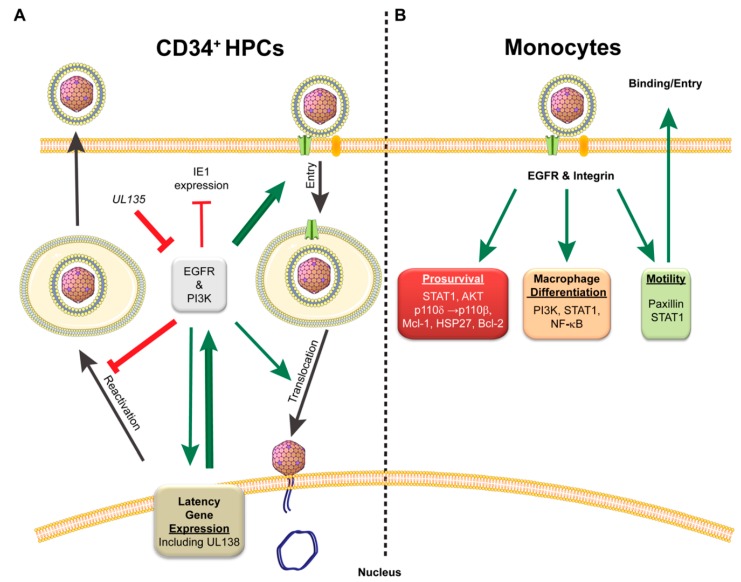
Figure 2.
Importance of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and integrin signaling during CMV latent infection. (A) EGFR signaling is important for CMV entry, translocation to the nucleus, and to establish latency. Attenuation of EGFR signaling by the UL135 proteins or inhibitors disrupts this pattern and contributes to reactivation of CMV replication. Thickness of arrows and lines depicts strength of supporting studies; (B) In monocytes, CMV binding and entry via EGFR and integrin receptors results in changes in signaling to promote cellular survival, macrophage differentiation, and motility to promote virus dissemination in the infected host. Red T bars indicate inhibition. Green arrows indicate activation.