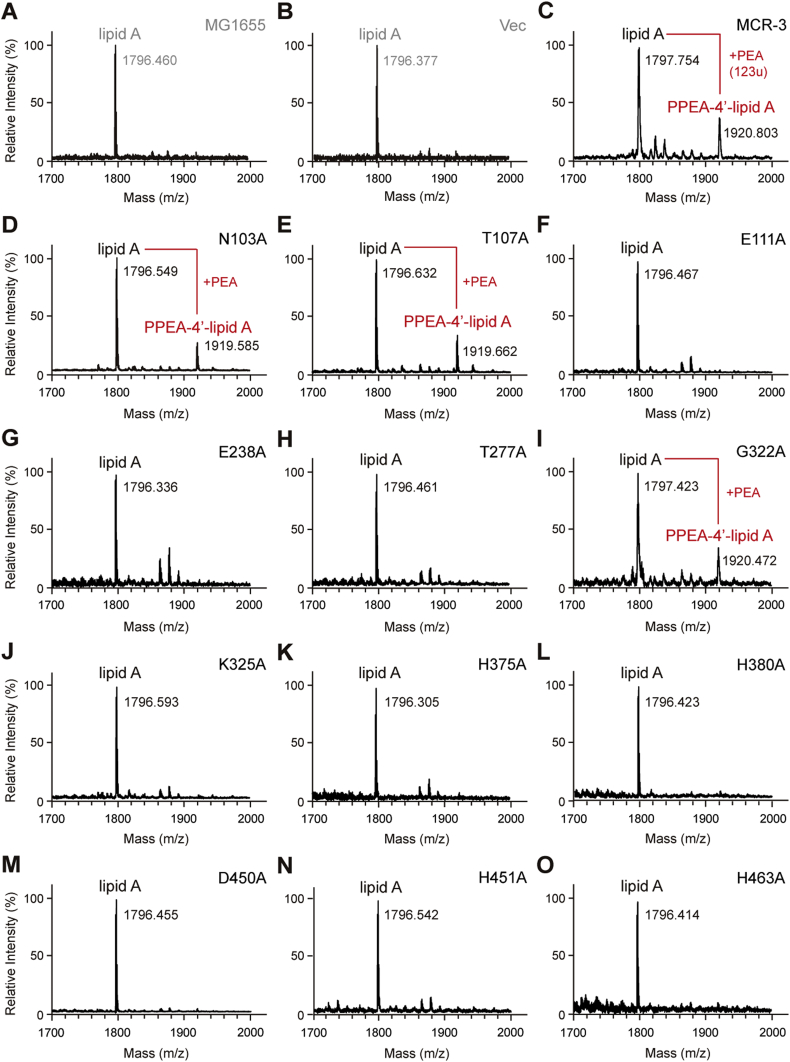
Fig. 7.
Metabolic evidence that the PE lipid substrate-interactive cavity of MCR-3 participates in chemical modification of the lipid A moieties of lipopolysaccharides in E. coli.
MALDI-TOF MS spectrum of the LPS-lipid A species isolated from the two negative controls, the E. coli strain MG1655 alone (A) and with the empty vector pBAD24 (B).
C. Expression of MCR-3 in E. coli leads to the appearance of an additional peak of PPEA-4′-lipid A, the modified form of lipid A.
The substitution of N103A (D) and T107A (E) in MCR-3 cannot completely impair the enzymatic activity in the structural modification of lipid A moieties.
MALDI-TOF MS analyses confirm that the three point-mutants of MCR-3 [namely E111A (F), E238A (G) and T277A (H)] are nonfunctional in the transfer of PEA to lipid A species.
I. The point mutation of MCR-3 (G322A) does not influence its enzymatic activity in the addition of PPEA to the 4′-phosphate group of lipid A moieties.
The six point-mutants of MCR-3 whose enzymatic activities are fully inactivated include K325A (J), H375A (K), H380A (L), D450A (M), H451 (N) and H463A (O), respectively.
The MS peak of lipid A species in E. coli is shown at m/z of 1796.305–1797.630, whereas its modified form occurs at m/z of 1919.585–1920.803, upon the presence of functional (and/or partial active) versions of mcr-3 in E. coli.