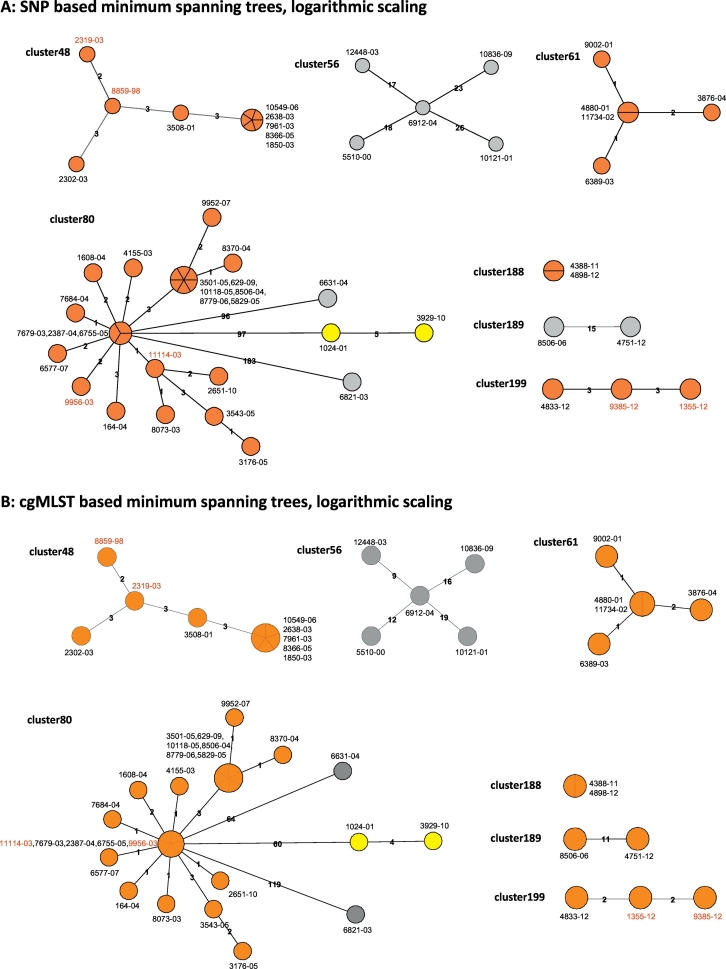
Fig. 3.
Comparison of the SNP and cgMLST approach employed for seven clusters defined by traditional genotyping methods for the Hamburg surveillance study. Minimum spanning trees built from either identified SNP positions (A) or from the cgMLST approach (B), shown in logarithmic scale. Colors indicate genomic clusters defined by a maximum distance of 12 SNP positions or allele variants, with orange and yellow denoting identified genomic clusters, and isolates marked in grey ungrouped. Isolates labeled in red exhibit differences between both approaches in their position in the derived tree.