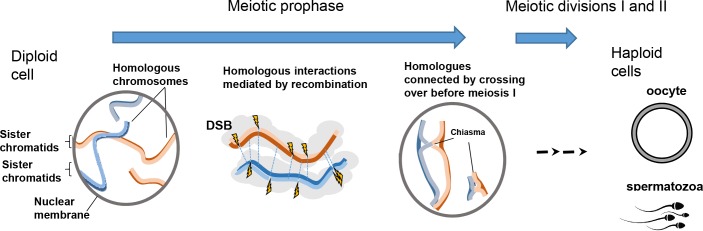
Fig 1. The role of homologous recombination during meiotic prophase.
During meiotic prophase, homologous recombination allows the interaction, alignment, and connection through chiasmata of homologous chromosomes. Chromosomes are structured by a protein axis (blue and red lines for paternal and maternal chromosomes, respectively) to which chromatin loops (grey cloud) are anchored. The recombination pathway is initiated by the formation of several DSBs (yellow lightning) on each homologue. DSB sites are determined by PRDM9. DSB repair promotes interactions between homologues (thin blue dotted lines). A small subset of DSB repair events, at least one per homologue pair, leads to a crossover visualized as a chiasma that establishes a topological connection between homologues. These connections are required for proper chromosome segregation at the first meiotic division (meiosis I). The two meiotic divisions lead to the formation of haploid oocytes and spermatozoa. DSB, DNA double strand break; PRDM9, PR domain-containing protein 9.