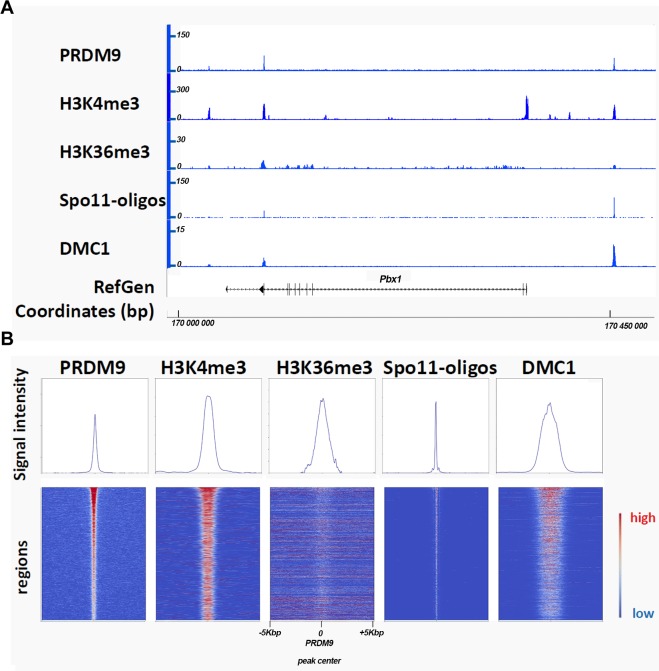
Fig 3. Sites of meiotic DSB formation.
(A) Detection of PRDM9, H3K4me3, H3K36me3, SPO11-oligos, and DMC1 in spermatocytes from C57BL/6 mice. A 500-kbp chromosomal region on mouse Chromosome 1 shows typical PRDM9-dependent DSB sites (1–2 kb wide) and enrichment for reads obtained after PRDM9 [59], H3K4me3 [77], H3K36me3 [59], and DMC1 [59] ChIP-Seq and after SPO11-oligo purification [64]. These sites also contain DNA sequences that share similarity with the PRDM9 consensus motif (PRDM9Dom2 in this case) (not shown). An annotated gene (Pbx1) and coordinates (bp) are shown in the lower part. (B) Average plots (upper panels) and heatmaps (lower panels) of PRDM9, H3K4me3, H3K36me3, SPO11-oligos, and DMC1 ChIP-Seq. 2,601 regions of PRDM9Dom2 (the PRDM9 allele expressed in C57BL/6) binding in the C57BL/6 strain [59] were pooled (average plots) or ranked relative to the strength of the PRDM9 signal. In the heatmaps, each line indicates a genomic region of 10 kbp centered on the peak of PRDM9 binding where the signal intensity along that region (reads recovered by NGS) is represented by a color code (red, highest signal; blue, lowest signal). H3K36me3 is blurred due to overlapping signals from transcription activity. The plots show the average values over the 10-kbp interval for all the 2,601 regions. DSB, DNA double strand break; ChIP-Seq, chromatin immuno-precipitation followed by sequencing; H3K4me3, histone H3 lysine4 trimethyl; NGS, next generation sequencing; PRMD9, PR domain-containing protein 9; SPO11, sporulation protein 11.