Fig 7. Evolution of PRDM9-binding sites.
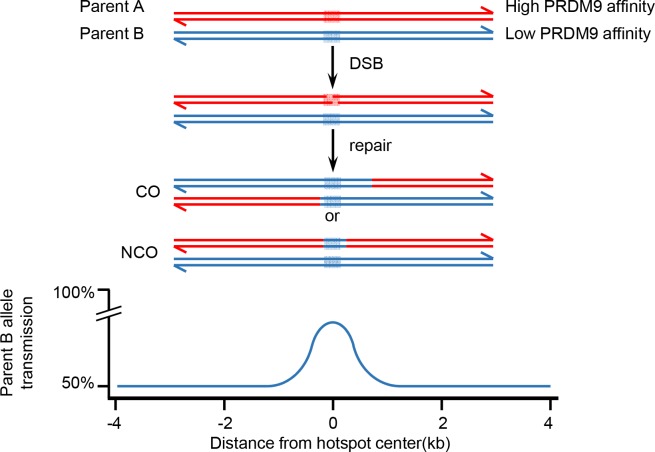
Mechanism of hotspot erosion by DSB-induced biased gene conversion. The repair by homologous recombination of a DSB leads to the replacement by gene conversion of the interval around the DSB site by the sequence from the unbroken chromatid. If two alleles with different affinity for PRDM9 are present in a population, this will result in overtransmission of the low-affinity site (blue shaded area) and erosion of the high affinity site (red shaded area). Therefore, the transmission frequency of alleles within and around PRDM9-binding sites can be higher than the 50% expected by Mendelian inheritance in the absence of bias. This effect is limited by the size of the gene conversion tracts (a few hundred bp) (lower panel). DSB, DNA double strand break; PRDM9, PR domain-containing protein 9.