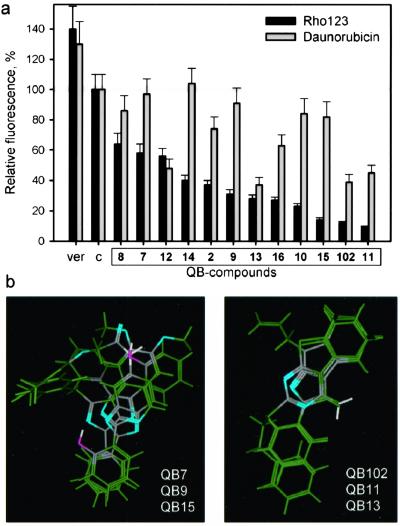
Figure 4.
Differences in the relative effect of isolated P-gp modulators on different P-gp substrates correlate with their structures. (a) Comparison of the effect of each P-gp modulator on efflux of daunorubicin and Rho-123. Dependence of modulating effect on the dose of the compounds was determined for each modulator. In all cases, the modulating effect determined as stimulation of Rho-123 and daunorubicin efflux reached a plateau at a concentration of 5–10 μM. There was no difference in the dose dependence of modulating effect estimated for Rho-123 and daunorubicin. Con A cells were incubated for 2 h with Rho-123 (1 μM) or daunorubicin (500 ng/ml) in the presence of the indicated compounds (10 μM), and accumulation of the drugs was quantitated by flow cytometry. The compounds are shown in the order of their relative strength in stimulating Rho-123 efflux in comparison to the accumulation of the drugs in the absence of the P-gp modulators (c) or in the presence of verapamil (ver). (b) Flexible alignments of three-dimensional models of the indicated compounds. Light blue regions symbolize hydrogen bond acceptors.