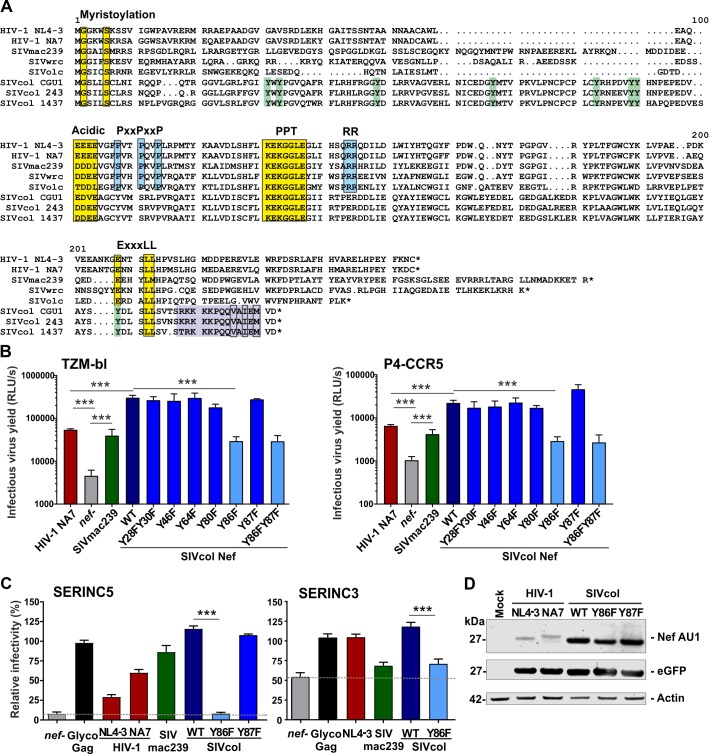
Fig 2. Y86 is critical for SERINC3/5 antagonism by SIVcol Nef.
(A) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of HIV and SIV Nef proteins. Dots indicate gaps. Functional amino acid motifs are highlighted. Y residues in SIVcol Nef that were mutated for functional analyses are indicated in green. (B) TZM-bl (left) or P4-CCR5 (right) indicator cells were infected with HIV-1 NL4-3 constructs containing the indicated HIV and SIV nef genes or a defective nef allele. Infections were performed in triplicate with three different virus stocks. Shown are mean values of the nine measurements +SEM. (C) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with HIV-1 NL4-3 constructs encoding indicated Nef and SERINC5 (left) or SERINC3 (right) or control plasmid. Shown are the mean levels of infectious virus production by the respective IMCs in the presence of transient SERINC5 or SERINC3 expression (+SEM; n = 9) relative to those obtained in cells transfected with the control vector (100%). Results were derived from three experiments, each using triplicate infection of TZM-bl cells to determine infectious virus yield. P-values represent reduction of infectious virus yield by SERINC expression or differences in susceptibility between wt and nef-defective HIV-1 IMCs. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. (D) Expression of HIV-1 and SIVcol Nef proteins. Western blot analysis of cell lysates following transfection of HEK293T cells with pCG vectors expressing AU1-tagged versions of the indicated Nef proteins. Actin and eGFP are shown as loading and transfection controls, respectively.