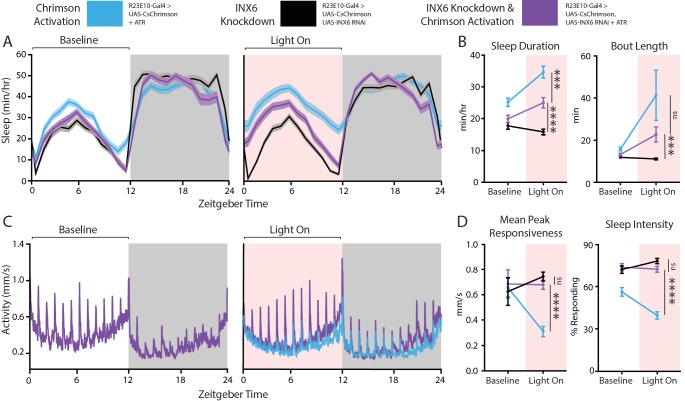
Figure 7. Behavioral effects of INX6 knockdown in activated R23E10 neurons.
(A–D) Three different behavioral conditions comparing flies with R23E10 neurons that can be activated (UAS-CsChrimson/+; R23E10-Gal4/+with ATR, blue, n = 50) with flies where R23E10 neurons cannot be activated but have INX6 knocked down (UAS CsChrimson/+; UAS-INX6 RNAi/R23E10-Gal4 no ATR, black, n = 51) and flies with R23E10 neurons that can be activated and have INX6 knocked down (UAS-CsChrimson/+; UAS-INX6 RNAi/R23E10-Gal4 with ATR, purple, n = 51) for effects on sleep and responsiveness following red light activation. (A) Mean sleep duration (min/hr, shading indicates SEM) during the 24 hr before red light activation, then during the next 24 hr during which red light is delivered for 12 hr during the day (pink shading). (B) Comparison between the 12-hr day period without red light (baseline) and the period of red-light activation in terms of sleep duration and bout length. (C) Mean activity (mm/s) for UAS-CSChrimson/+; UAS-INX6 RNAi/R23E10-Gal4 with ATR for the same time periods as (A). UAS-CsChrimson/+; R23E10-Gal4/+ with ATR is overlaid (blue) during the 'Light On' period to show differences in responses to hourly stimuli. Other traces (black) not shown for clarity; see (D) for summarized control data. (D) Comparison between the 12-hr day period without red light (baseline) and the period of red-light activation in terms of peak responsiveness and sleep intensity. Error bars indicate SEM and asterisks indicate significance (***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, t-tests).