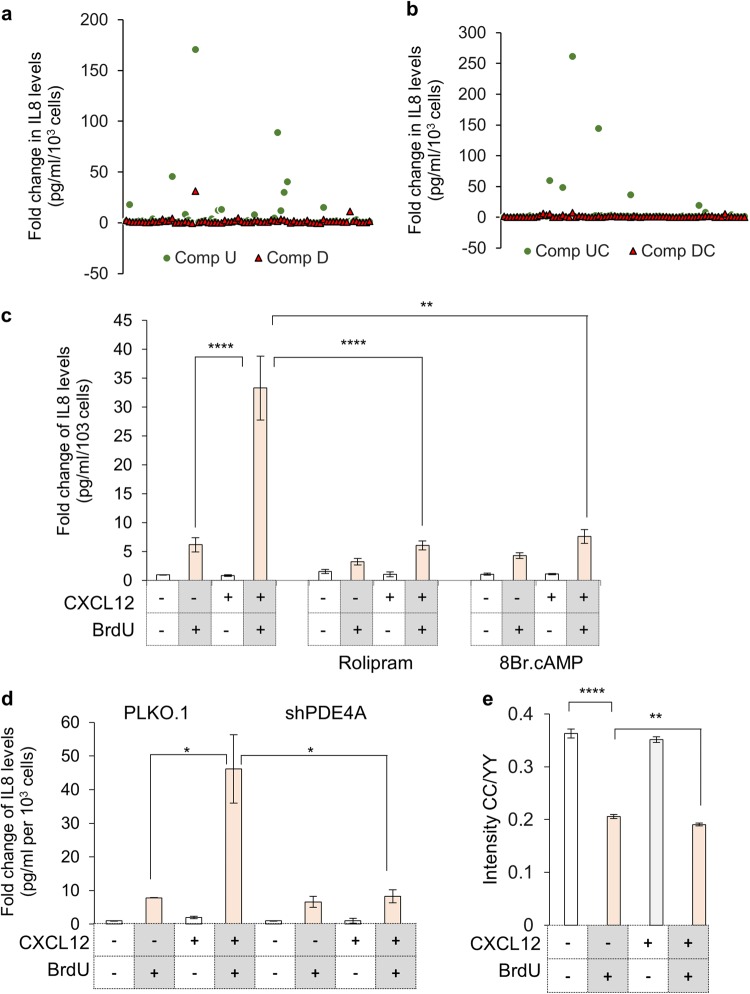
Fig. 5.
Identification of signaling cascade involved in CXCR4-activation dependent enhanced inflammation during DNA damage. a Screening for compounds modulating DNA damage associated inflammation. Scatter plot for individual compounds in LOPAC plate 1 representing fold change of IL8 secretion (through ELISA) when compared to untreated (Comp U, circle) or damaged cells (Comp D, triangle). b Scatter plot of compounds modulating CXCR4 activation dependent enhanced DNA damage-associated inflammation. Scatter plot for individual compounds from LOPAC plate 1, representing fold change of IL8 levels (through ELISA) compared to CXCL12 stimulated cells which are untreated (Comp UC, circle) or in presence of DNA damage (Comp DC, triangle) is shown. c Role of cAMP modulators on CXCR4 dependent enhanced inflammatory response. The media from treated HeLa cells (as indicated) was used for determining IL8 levels compared to untreated control cells (n = 3). d Effect of PDE4A expression knockdown on CXCR4 activation dependent inflammation. The media from treated and untreated HeLa cells transfected with shRNAs as indicated was used to determine levels of IL8 (n = 4). e Measurement of cAMP levels in CXCL12 treated damaged cells. FRET ratios recorded by measuring CC/YY intensity changes in ICUE3 reporter in HeLa cells treated as indicated (Cell images are shown in Supplementary Figure S5d). For all experiments results are shown as mean ± s.e.m. *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.01; ****p ≤ 0.001 (Student’s t-test; n = 3)