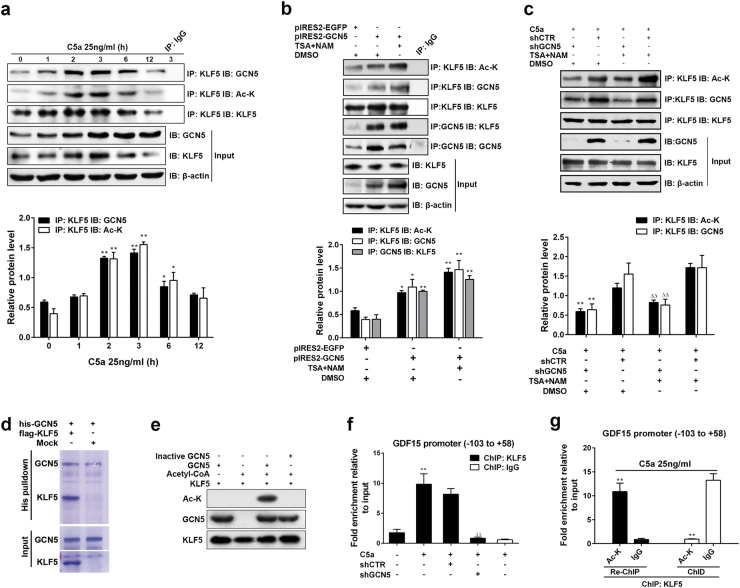
Fig. 5.
The GCN5–KLF5 interaction and KLF5 acetylation upon C5a stimulation or change of GCN5, and the effect of KLF5 acetylation by GCN5 on binding to GDF15 promoter. a IP-IB was done by using abs against KLF5 and GCN5. The related level of KLF5 acetylation and GCN5–KLF5 binding was adjusted to precipitated total KLF5. It showed that C5a could enhance GCN5–KLF5 binding and KLF5 acetylation in A549 cells at 2, 3, and 6 h (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. 0 h). b A549 cells transfected with pIRES2-GCN5 for 48 h were then treated with (or without) trichostatin A (TSA, 1 μM) and nicotinamide (NAM, 5 μM) for 6 h. By IP, the level of GCN5–KLF5 combination or KLF5 acetylation was upregulated after GCN5 overexpression, which was more significant in the present of TSA and NAM (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. pIRES2-EGFP + DMSO). c A549 cells transfected with shGCN5 for 48 h were treated with TSA and NAM for 6 h, followed by C5a for 3 h. IP exhibited a notable decrease of GCN5–KLF5 binding and KLF5 acetylation, even with TSA and NAM treatment (**P < 0.01 vs. shCTR + C5a + DMSO, △△P < 0.01 vs. shCTR + C5a + TSA + NAM). d The his-GCN5 protein was bound to the cobalt-coated beads, followed by purified flag-KLF5 incubation. The pulldown mixture was subjected to SDS-PAGE and coomassie blue staining. The result showed GCN5 could directly bind to KLF5. Mock: elution from anti-flag affinity gel incubated with the cell lysate without flag-KLF5. e Purified KLF5 was incubated with acetyl-CoA and active or inactive GCN5. The acetylation of KLF5 was measured by IB using the acetylated lysine antibody. It showed that the active GCN5 but not inactive GCN5 could acetylated KLF5. f The ab against KLF5 was employed to perform ChIP assay, and real-time PCR displayed that the binding of KLF5 on GDF15 promoter region (−103 to + 58 nt) in C5a group was higher than DMEM group (**P < 0.01), but the binding level in shGCN5 + C5a group markedly dropped compared with shCTR + C5a group (△△P < 0.01). g A549 cells were exposed to C5a stimulation for 3 h. The ChIP assay was performed with anti-KLF5, followed by the Re-ChIP assay with anti-Ac-K. Purified DNA in the precipitation and supernatant were then amplified by real-time PCR to detect GDF15 promoter fragment. Re-ChIP proved the enrichment of acetylated KLF5 in GDF15 promoter was greatly increased, while ChID showed that GDF15 promoter fragment was significantly diminished in the supernatant after Re-ChIP (**P < 0.01 vs. IgG). Representative photographs are showed. Data are expressed as means ± S.E.M. from at least three independent experiments