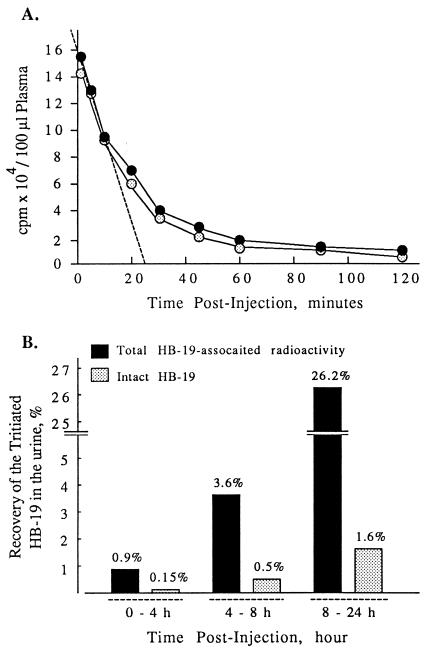
Figure 3.
The pharmacokinetic properties of HB-19 in the blood and urine. Rats were injected intravenously with 20 μg (1.8 MBq or 50 μCi) of the [3H]-labeled HB-19. (A) For the plasma distribution profile of [3H]-labeled HB-19, blood was collected at selected times from 2–120 min and the total plasma radioactivity (closed circles) and the amount of the intact HB-19 were determined (open circles). The intact peptide was measured after RP-HPLC analysis as described in Materials and Methods. (B) The in vivo elimination of the 3H-labeled HB-19 was investigated by measuring radioactivity excreted in the urine collected at 0–4 h, 4–8 h, and 8–24 h. The % of total HB-19-associated radioactivity (black histograms) and the % of the intact [3H]-labeled HB-19 (gray histograms) corresponding to the RP-HPLC peak of HB-19 in the urine at each point were calculated in respect to the radioactivity injected.