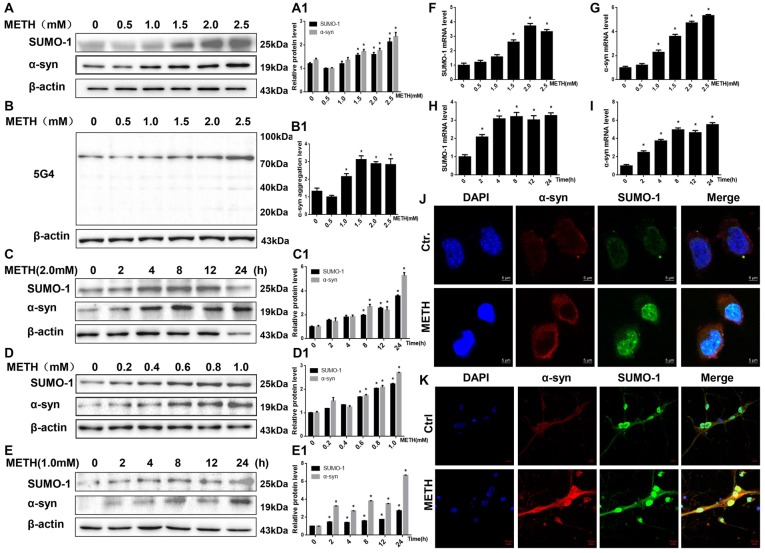
Figure 1.
Methamphetamine (METH) increases small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 (SUMO-1) and alpha-synuclein (α-syn) protein expression in vitro. METH exposure up-regulates the protein expression of SUMO-1, α-syn and the aggregation of α-syn in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner in SH-SY5Y cells and primary cultured neurons. SH-SY5Y cells were exposed to 0.5 mM-2.5 mM METH for 24 h (A,B,A1,B1) and 2.0 mM METH for 2–24 h (C,C1). Primary cultured neurons were exposed to 0.2–1.0 mM METH for 24 h (D,D1) and 1.0 mM METH for 2–24 h (E,E1). Western blot (A–E) and quantitative analyses (A1–E1) were performed to determine the levels of SUMO-1, α-syn and aggregated α-syn. RT-QPCR (F–I) was performed to determine SUMO-1 and α-syn mRNA expression in SH-SY5Y cells. SUMO-1 and α-syn were expressed at higher levels in METH-treated SH-SY5Y cells (2.0 mM, 24 h) and primary cultured neurons (1.0 mM, 24 h) than in the control group, according to analysis with a fluorescence microscope (J,K). SUMO-1 was stained with anti-SUMO-1 antibody (green); α-syn was stained with anti-α-syn antibody (red); nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). β-Actin was used as a loading control. *p < 0.05 compared with the control group. The data shown in (A–I) were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by least significant difference (LSD) post hoc analyses.