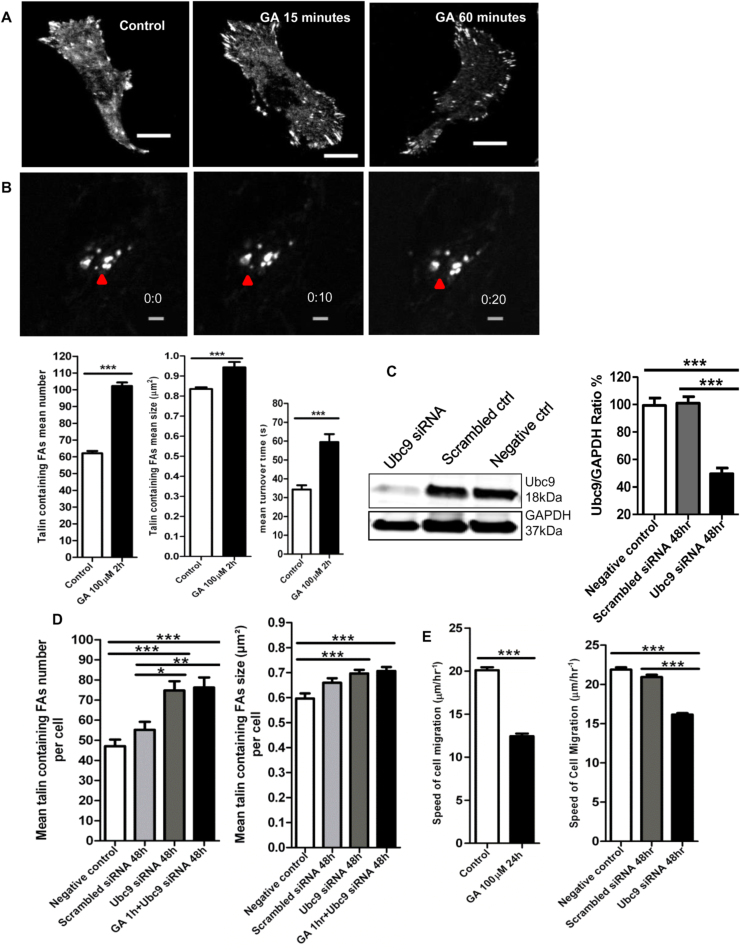
Fig. 1.
Inhibiting SUMOylation increases the number, size and turnover of focal adhesions and reduces the speed of cell migration in MDA-MB-231 cells. 1A. MDA-MB-231 cells were grown on 0.2% gelatin-coated glass coverslips. Immunostaining of talin containing FAs were shown in the control or after 15 or 60 min of 100 µM GA treatment (scale bar = 20 µm). 1B. MDA-MB-231 cells were grown on top or at the edge of 2 mg/ml rat tail collagen I (scale bar = 10 µm). GFP-talin containing FAs were shown in untreated live MDA-MB-231 cells establishing the dynamic turnover of FAs. The red arrow indicates a single talin-containing FA was turning over in 10 s, initially appearing at 0 s, continuing to be present for 10 s and disappearing at 20 s. In this live-cell GFP-FA turnover assay, 2 h of 100 µM GA treatment increased the mean number, size or turnover time of talin containing FAs (n = 5, individual replicates, data shown as mean ± SEM, p < 0.0001 ***, two-tailed unpaired t-test, >300 cells were counted either for the control or the GA treatment in the mean number and size of FAs; for turnover rate, 280 or 182 adhesion number was counted for the control or the GA treatment manually). 1C. 48 h of 25 nM Ubc9 siRNA treatment caused knockdown of Ubc9 E2 enzyme, the bar chart is presented as Ubc9 vs. GAPDH ratio (n = 4, individual replicates, data as mean ± SEM, p < 0.0001 ***). 1D. MDA-MB-231 cells were grown on 0.2% gelatin-coated glass coverslips. 48 h of 25 nM Ubc9 siRNA treatment increased the mean number or size of talin containing FAs (n = 4, individual replicates, data as mean ± SEM, p < 0.0001 ***, one-way ANOVA with post-hoc test, 255, 173 and 240 cells were counted for negative control, scrambled siRNA or Ubc9 siRNA treatment); although there was no further increase in the combination treatments using GA with Ubc9 siRNA together. 1E. MDA-MB-231 cells were grown in 2 mg/ml rat-tail collagen I. 24 h of 100 µM GA treatment decreased the speed of cell migration significantly (n = 3, individual replicates, mean ± SEM, p < 0.0001 ***, two-tailed unpaired t-test, 361 or 273 cells were counted for the control or the GA treatment). 48 h of 25 nM Ubc9 siRNA decreased the speed of cell migration significantly (n = 4, individual replicates, mean ± SEM, p < 0.0001 ***, one-way ANOVA with post-hoc test, 550 > cells were analysed either for the control or the siRNA/scrambled siRNA treatment).