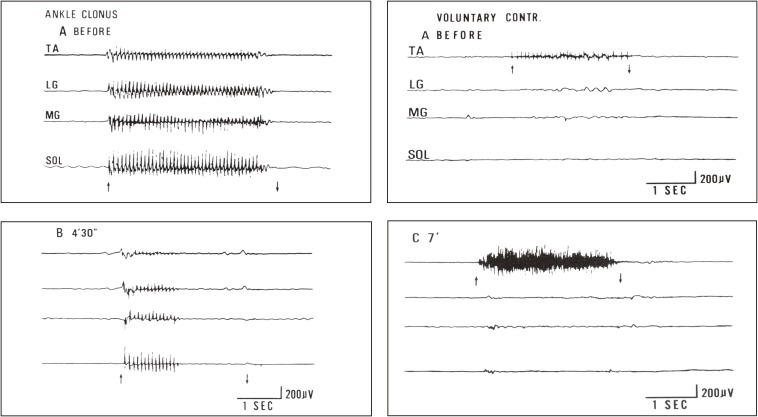
Figure 23.
Effects of nerve block to spastic muscles in capsular hemiplegia. Changes in ankle clonus (left figures) and voluntary muscle power in pretibial muscles (right figures) before (A) and after (B, C) nerve block to motor points of the medial and lateral gastrocnemius muscles are shown. Simultaneous recording from four muscles using wire electrodes. From top downwards; TA: tibialis anterior. LG: lateral gastrocnemius. MG: medial gastrocnemius. SOL: soleus muscles. Left figures: EMG of leg muscles during stretching to evoke maximal ankle clonus (between arrows). Records before (A) and 4.5 min after (B) injection of 1 ml of 50% ethyl alcohol into the gastrocnemius motor points. Right figures: EMG of leg muscles at maximal voluntary contraction of the pretibial muscle (TA) before (A) and 7 minutes after (C) alcohol block of the lateral and medial gastrocnemius muscles. After extensor (gastrocnemius) block, a marked increase in EMG and actual strength occurred in the flexor pretibial muscle (TA), whereas the blocked gastrocnemius muscle showed no reduction in strength but resulted in smoother contraction. (From Yanagisawa, Tanaka and Ito, 197670)).