Figure 8. Hypothesized anti‐adhesive mechanisms by which TNX supports the motor function.
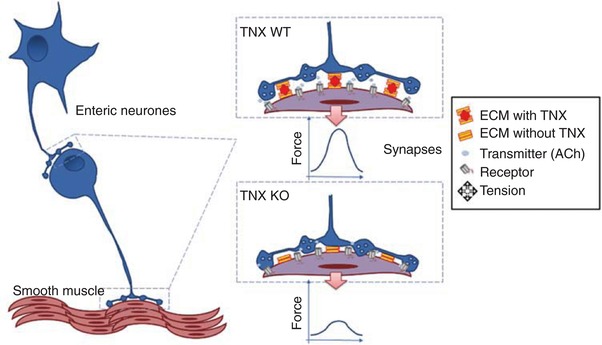
In the colon, TNX acts to maintain correct orientation and spacing of synaptic contacts at neuronal and neuromuscular junctions. Thus, the release of neurotransmitter is able to reach the postsynaptic receptor and engage effectively with it, giving rise to an optimal contractile response to neural activation. Without TNX, these junctions are disorganized, possibly by being too narrow, and fail to allow efficient neurotransmission.
