Figure 2. The non‐halide thiocyanate (SCN−) increases anion transport rate in ClC‐5/3 wild‐type and E224A Gluext mutant.
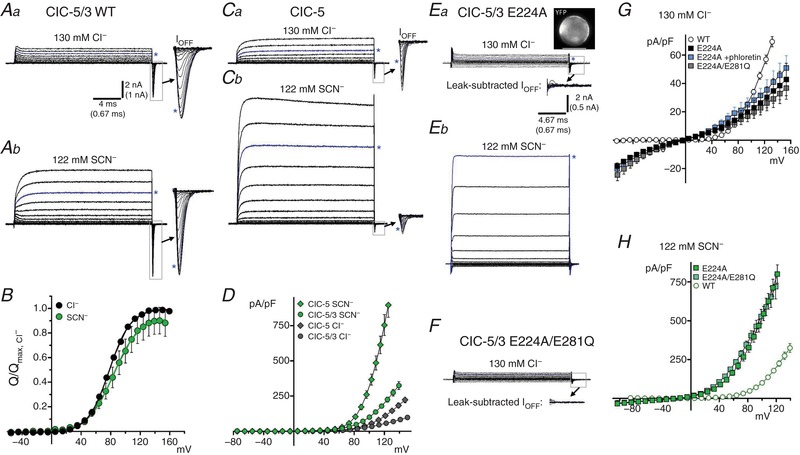
A, ClC‐5/3 steady‐state (I SS) transport and transient gating currents in normal (a, 130 mM Cl−, pH 7.35) and SCN−‐containing (b, 122 mM SCN−/8 mM Cl−; pH 7.35) external saline. I SS traces are displayed up to +140 mV depolarization. I Off transients (boxed regions) are shown at expanded scale to the right (arrows; displayed to +160 mV). Asterisks (blue traces) indicate currents at +115 mV. SCN− greatly increases I SS, consistent with increased anion “slippage”. B, Q Off–V relationships for ClC‐5/3 in Cl− and SCN−‐containing saline, normalized to same‐cell values in Cl−. Continuous lines show fits to Boltzmann functions. Relative Q max is not significantly altered in SCN−, while V 1/2 of Q–V is shifted by +6 mV (see Table 1). C, ClC‐5 I SS and transient gating currents in Cl− (a) and SCN−‐containing external saline (b), showing a large increase in SCN− current magnitude. I SS traces are displayed up to +140 mV as in A; I Off transients expanded to the right (arrows) are displayed to +180 mV (scale as in A). Asterisks (blue traces) indicate current trace recorded at +120 mV. I Off in SCN− (b) is likely obscured due to the extremely large I SS magnitude (see Methods). D, I SS–V relationships compared for ClC‐5/3 and ClC‐5 in external Cl− and SCN−. SCN− produces a larger‐fold increase in ClC‐5 currents. Untransfected HEK cells exhibit a significant endogenous SCN− conductance (29 pA/pF at +115 mV; see Table 1). E, unsubtracted currents in external Cl− (a) and SCN− (b) in an E224A mutant‐expressing cell; dashed line indicates zero‐current level. Image (top right) shows YFP protein expression in the recorded cell. E224A abolishes voltage‐dependent transient charge movements and results in a loss of I SS rectification and decreased current amplitudes at depolarized voltages. Lower inset in Ea shows leak‐subtracted currents at a magnified scale from the indicated boxed region. E224A transport is dramatically increased in external SCN− (b; non‐subtracted traces are displayed up to +120 mV). F, E22A/E281Q double mutant currents are essentially indistinguishable from E224A; scale of currents and magnified inset as in E, top. Dashed line indicates zero‐current level. G, I SS–V relationships in external Cl− for E224A single and E224A/E281Q double mutants (filled and shaded symbols), compared to wild‐type ClC‐5/3 (WT, open symbols). The Cl− channel blocker phloretin (100–150 μM) produces no significant block of E224A currents. H, I SS–V relationships in external SCN− for E224A mutants (shaded symbols) compared to wild‐type. E224A mutation impairs maximal Cl− transport, but greatly facilitates SCN− transport. [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
