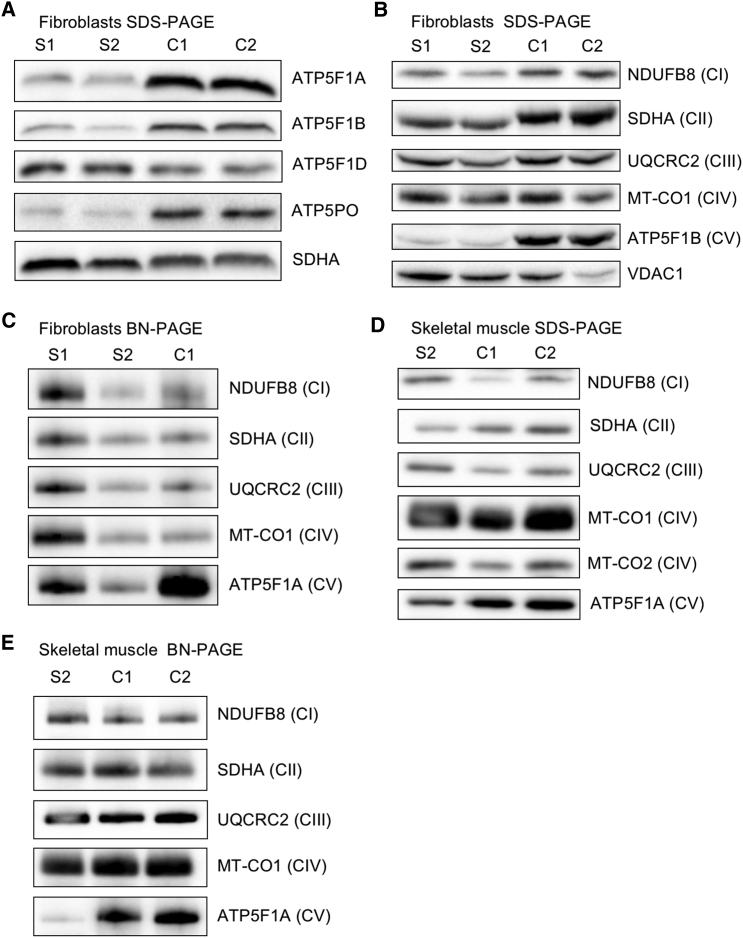
Figure 2.
Biallelic Variants in ATP5F1D Impair the Steady-State Amounts of the F1FO ATP Synthase Complex and Subunits
Immunoblot and BN-PAGE analysis were carried out on subject cultured skin fibroblasts and skeletal muscle samples as previously described.11, 17, 18 SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis of whole-cell lysates (40 μg) isolated from cultured skin fibroblasts of affected subjects 1 (S1) and 2 (S2) and age-matched control individuals show (A) the steady-state amounts of complex V subunits (ATP5F1A, ATP5F1B, ATP5F1D, and ATP5PO) and (B) the amounts of individual OXPHOS complex subunits. One-dimensional BN-PAGE analysis was performed for assembled OXPHOS complexes in n-dodecyl-β-D-maltoside (DDM; 850520P, Sigma)-solubilized mitochondrial extracts isolated from control, S1, and S2 fibroblasts (C). Steady-state amounts (D) and assembly (E) of OXPHOS complexes and subunits in DDM-solubilized mitochondrial extracts from control and subject 2 skeletal muscle demonstrate a decrease in complex V. In (C) and (E), mitochondrial lysates (100 μg) were loaded on a 4%–16% native gel (Life Technologies), and then protein complexes were immobilized onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes and subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated OXPHOS-subunit-specific antibodies. In (A)–(E), nuclear-encoded SDHA (ab14715, Abcam) or porin (VDAC1, ab14734, Abcam) was used as a loading control. Abbreviations are as follows: BN, blue native; CI, complex I; CII, complex II; CIII, complex III; CIV, complex IV; and CV, complex V.