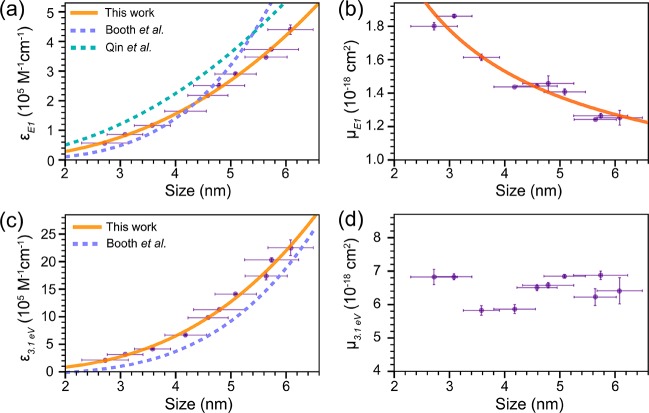
Figure 5.
(a) Size-dependent molar absorption coefficients εE1 at the first exciton transition energy (E1) of nearly spherical wz CIS QDs (In/Cu = 0.91 ± 0.11). The orange solid line is a fit to the data using a power law function (eq 6). Purple and green dashed lines denote the size-dependent trends reported in the literature for pyramidal cp CIS QDs (In/Cu = 0.91 and ∼1).51,52 (b) Size-dependent absorption cross-section per formula unit at E1(μE1) of wz CIS QDs (In/Cu = 0.91 ± 0.11). The orange solid line is a fit to the data using a power law function (eq 9). (c) Size-dependent molar absorption coefficients ε3.1 eV at 3.1 eV of wz CIS QDs (In/Cu = 0.91 ± 0.11). The orange solid line is a fit to the data using a power law function (eq 11). The purple dashed line denotes the size-dependent trend reported in the literature for pyramidal cp CIS QDs (In/Cu = 0.91) by Booth etal.52 (d) Size-dependent absorption cross-section per formula unit at 3.1 eV (μ3.1 eV) of wz CIS QDs (In/Cu = 0.91 ± 0.11).