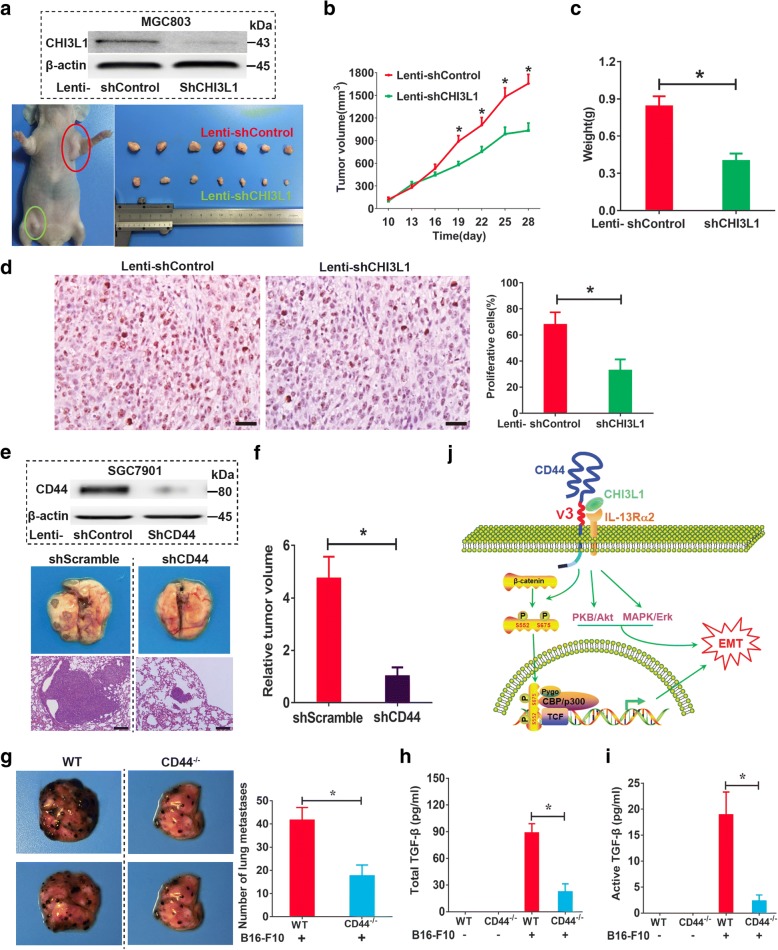
Fig. 7.
CHI3L1 mediated tumorigenesis through CD44 in vivo. a A representative image of tumor growth in nude mice subcutaneously inoculated with lenti-shCHI3L1- or lenti-shControl-transfected MGC803 cells. b The growth curve of subcutaneous tumor from MGC803 cells infected with lenti-shCHI3L1 or lenti-shControl in nude mice (n = 10 animals per group). c Comparison of tumor weight from two groups at the end of the experiment. d Evaluation of cell proliferative activity by Ki-67 staining in subcutaneous xenografts from MGC803 cells infected with lenti-shControl or lenti-shCHI3L1. e and f H&E staining of the representative SGC7901 cells lung metastatic lesions in nude mice (e). The total area of invasive lesions on the lung slice section represents the invasive tumor volume in the lungs (f). Sizing bar indicates 100 μm. g Representative photograph of lungs from WT and CD44−/− mice 2 weeks after challenge with B16-F10 melanoma cells. Comparison of the number of pleural melanoma colonies in lungs from tumor cells challenged WT and CD44−/− mice (n = 8 animals per group). h and i The levels of total (h) and active (i) TGF-β1 in broncho-alveolar lavage (BAL) fluids from WT mice and CD44−/− mice. j Schematic representation of the CHI3L1/CD44-IL-13Rα2 signaling pathway in promoting GC cell metastasis. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05 (Student’s t test)