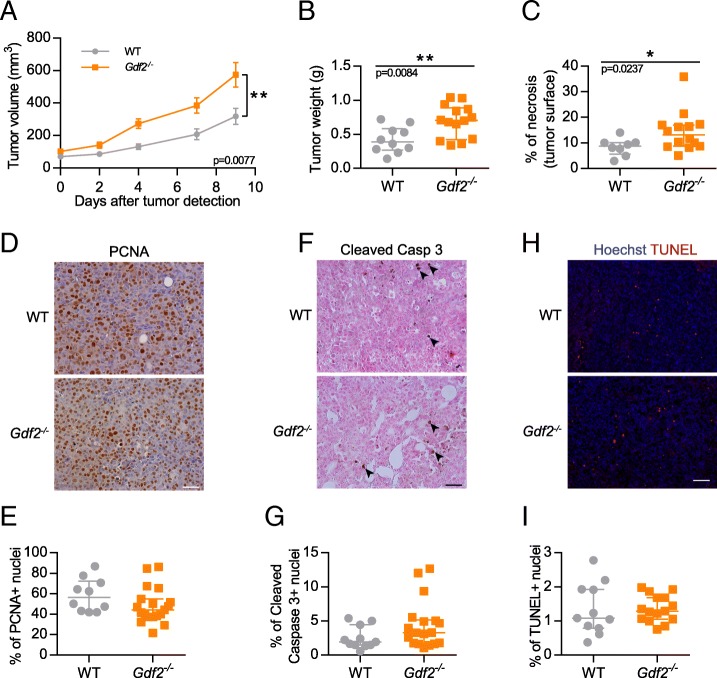
Fig. 1.
Gdf2 deletion increases tumor growth in the E0771 mammary cancer model. E0771 cells were injected in the 4th mammary gland and tumor growth was assessed by caliper measurement every 2 to 3 days after tumor detection (a) and tumor weight measured (b) at the end of the experiment, 9 days after tumor detection (WT n = 10, Gdf2−/− n = 14, 1 representative experiment out of 4). c Tumor necrosis area quantification (% of total tumor area) (WT n = 8, Gdf2−/− n = 14, 2 experiments). d-i Representative images and quantitative analysis of the tumors stained for PCNA (d, e), cleaved-caspase 3 (black arrowheads f, g), (WT n = 11, Gdf2−/− n = 18, 2 experiments). Scale bar 50 μm), and TUNEL (h, i) (WT n = 11, Gdf2−/− n = 15, 1 experiment. Scale bar 100 μm) (a) Data are the mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis: Two-way matched ANOVA. (b, c, e, g, i) Data are the median ± interquartile range. Statistical analysis: Mann-Whitney test. *p ≤ 0.05 and **p ≤ 0.01 significantly different