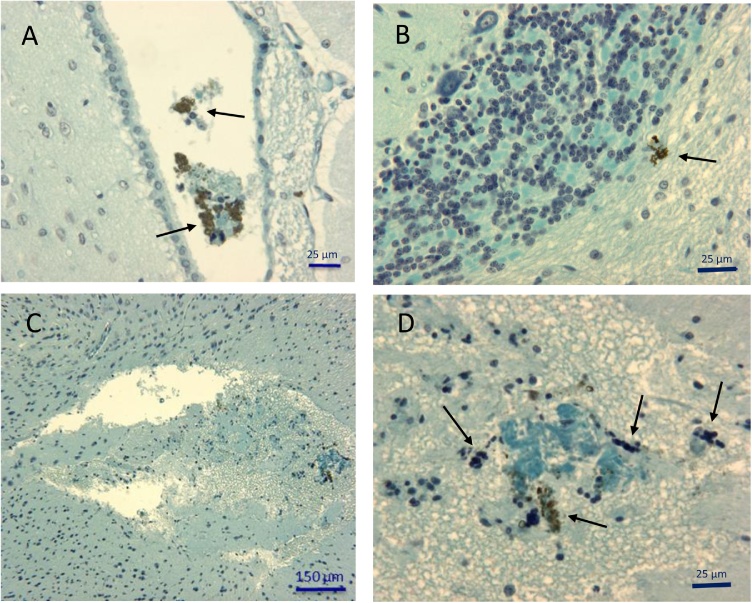
Fig. 8.
Illustration of histological alterations present in brain of rats exposed to TiO2 nanoparticles administrated at 16 g/kg B.W. (A) or 4 g/kg B.W. (B,C,D) and euthanized 1 month after the administration of the treatment. (A) Aggregates of nanoparticles (arrows) accompanied by cell fragments and inflammatory cells are present in cerebrospinal fluid inside cerebral ventricles. (B) Some scattered deposits of TiO2 are evidenced in the white matter of cerebellum. (C) Low magnification illustrating a large edematous and partially necrotic area in the white matter of brain. At higher magnification (D) the edema was accompanied by TiO2 aggregates (arrows) and also some fibrous material stained in blue and inflammatory cells mainly identified as lymphocytes and granulocytes.