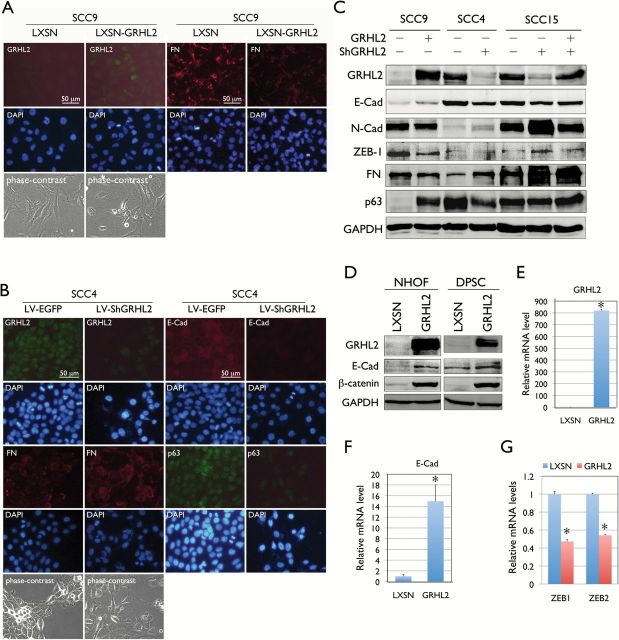
Figure 4.
GRHL2 regulates epithelial plasticity in OSCC. (A) Immunofluorescent staining was performed in SCC9 cells with or without GRHL2 overexpression using the retroviral vector, LXSN-GRHL2. GRHL2 overexpression and repressed FN expression were confirmed in SCC9/GRHL2 cells after G418 selection compared with the empty vector (LXSN) control. (B) Immunofluorescent staining was performed in SCC4/EGFP and SCC4/ShGRHL2 cells for GRHL2, E-Cad, p63 and FN. GRHL2 knockdown led to loss of E-Cad and p63 levels, while FN was induced. Phase contrast views for each cell group were shown. (C) GRHL2 expression levels were altered in SCC9, SCC4 and SCC15 cell lines by either overexpression (in SCC9) or knockdown (in SCC4 and SCC15). Alteration of GRHL2 level led to corresponding changes in proteins involved in epithelial (e.g. E-Cad and p63) and mesenchymal (e.g. N-Cad, ZEB1 and FN) phenotypes. In SCC15 cells, GRHL2 was re-expressed by retroviral vector (LXSN-GRHL2) infection after lentivirus-mediated GRHL2 knockdown. GRHL2 re-expression partially restored the epithelial phenotype, e.g. loss of N-Cad and ZEB1. (D) Ectopic GRHL2 expression in NHOF and DPSC enhanced the expression of E-Cad and β-catenin, which make up the epithelial adherens complex. (E-G) Expression levels of E-Cad, ZEB1 and ZEB2 were determined by qRT-PCR in SCC9 with or without GRHL2 transduction by retroviral vector (LXSN-GRHL2). Bars indicate standard deviation and asterisk (*) indicates statistical significance (P < 0.05), compared with the mean values of their control cells.