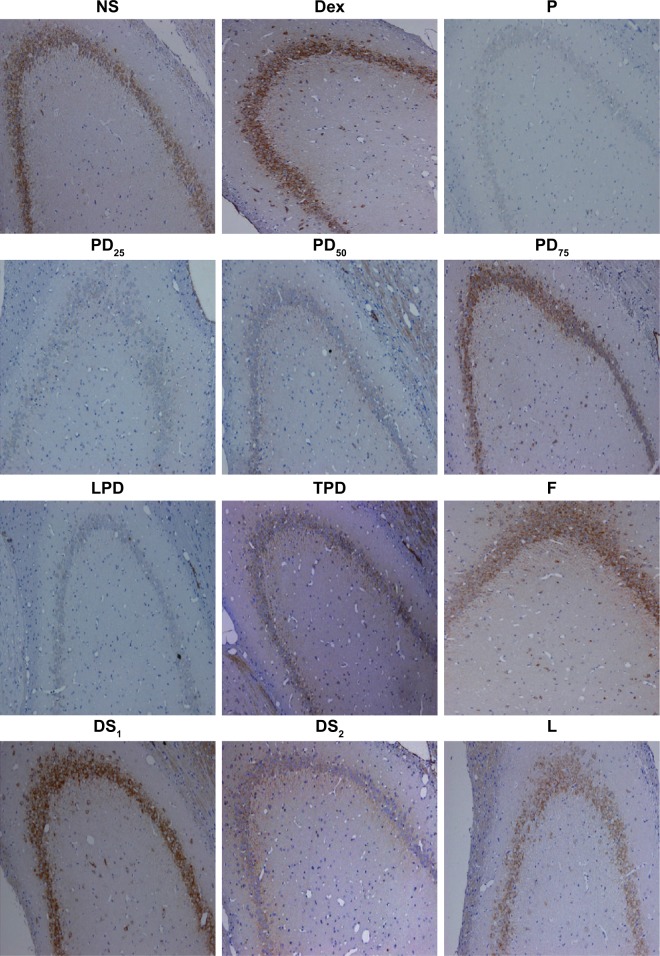
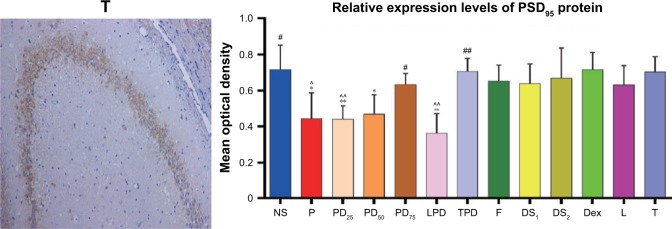
Figure 5.
Pretreatment of young rats with Dex attenuated the propofol-induced long-term neurotoxicity and increased the levels of PSD95 expression in the hippocampus in adult age.
Notes: P group: i.p. injected with 50 mg/kg propofol, and 40–60 min later, when the righting reflex was recovered, the procedure was repeated one more time; PD25, PD50 and PD75 groups: intraperitoneal injection with 25, 50 and 75 μg/kg Dex, and 30 min later, intervention with propofol; LPD group: intracerebroventricular injection with 25 μg/5 μL LY294002, and 30 min later, intervention with Dex and propofol; TPD group: intraperitoneal injection with 1 mg/kg TDZD-8, and 30 min later, intervention with Dex and propofol. DS1 and DS2 groups: intracerebroventricular or intraperitoneal injection with DMSO; F group: intraperitoneal injection with intralipid; L group: intracerebroventricular injection with LY294002; T group: intraperitoneal injection with TDZD-8; Dex group: intraperitoneal injection with Dex. The levels of PSD95 expression in the hippocampus of individual rats were examined by immunohistochemistry using anti-PSD95, HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies and DAB. Data are representative images (magnification ×200) or are expressed as the mean±SEM of each group (n=5 per group) from three separate experiments. *p<0.05 versus NS group; #p<0.05 versus P group; ^p<0.05 versus PD75 group; double symbols mean p<0.01.
Abbreviations: DAB, 3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride; Dex, dexmedetomidine; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; HRP, horseradish peroxidase; SEM, standard error of the mean.