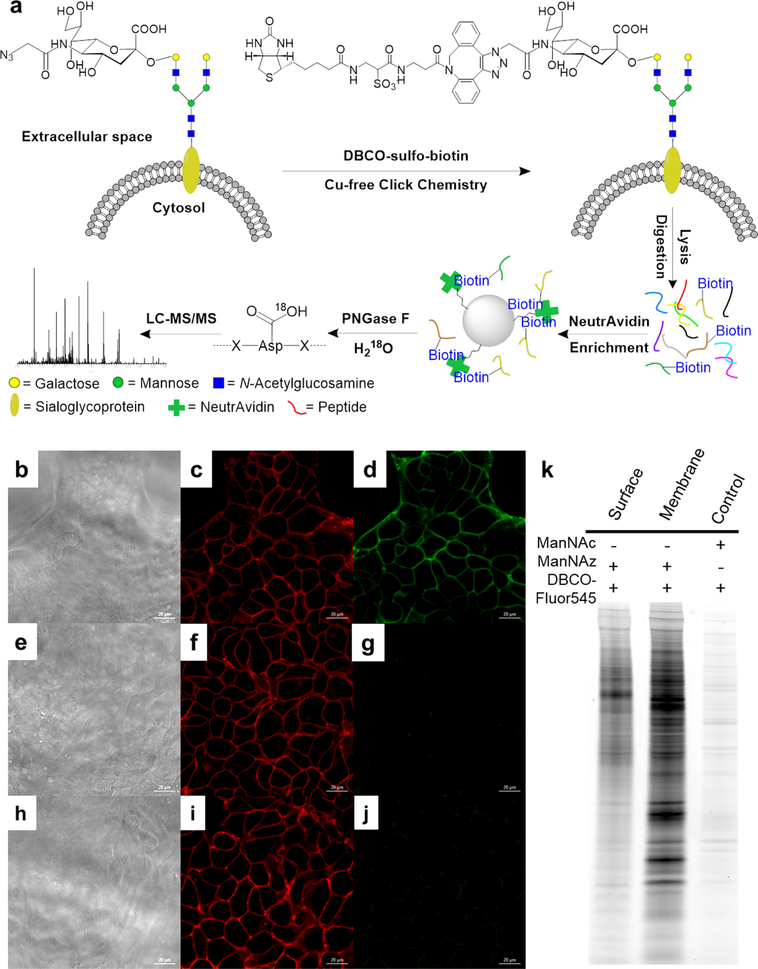
Figure 5.
(a) Principle of the site-specific identification of the surface N-sialoglycoproteome. (b−j) Microscope images of tagging sialoglycoprotein on the HEK 293T cell surface: (b, e, h) images of cells (scale bar is 20 μm); (c, f, i) fluorescence signals of labeled cells reacted with DBCO−Fluor545; (d) fluorescence signals of labeled cells bound to DBCO−sulfo−biotin, followed by streptavidin−FITC; (g) cells without the biotin tag treated with streptavidin−FITC show no green signal; (j) after surface sialoglycoproteins were tagged with DBCO−Fluor545, cells were further treated with DBCO−sulfo−biotin followed by streptavidin−FITC, but no green signals were detected. (k) Gel results for metabolic labeling and click chemistry. The control sample was from unlabeled cells. Reproduced with permission from ref 48. Copyright 2015 Royal Society of Chemistry.