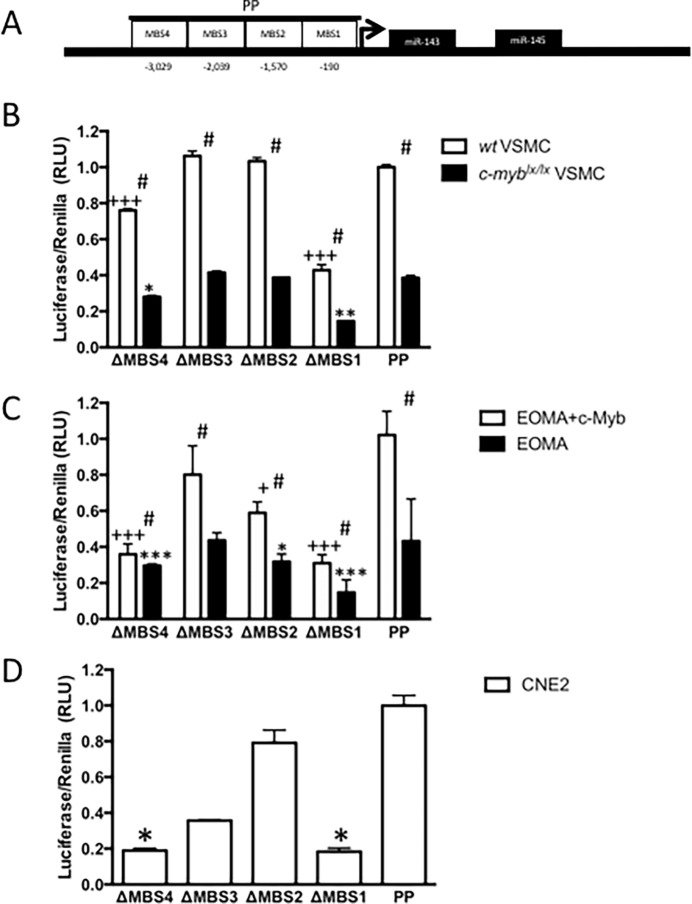
Fig 2. miR-143/145 promoter activity requires c-Myb binding sites (MBS).
Promoter activity was determined by co-transfection with promoter-luciferase constructs and renilla control plasmid. Site-directed mutagenesis revealed MBS to be important for reporter gene activation when compared to intact proximal promoter. (A) Proximal promoter (PP) with c-Myb binding site (MBS) positions shown relative to predicted transcriptional start. (B) Promoter luciferase constructs were transfected in c-myblx/lx VSMC or wt controls. Compared to proximal promoter, MBS1 (p<0.001+++) and MBS4 (p<0.001+++) were required for c-Myb-dependent transcription in c-myblx/lx VSMC (n = 3), both MSB1 (p<0.01**) and MBS4 (p<0.05*) were also required for transcriptional activity in wt VSMC (n = 3). Importantly, activation in wt was always greater than in c-myblx/lx VSMC (p<0.05). (C) In EOMA, an endothelial cell line that does not express c-Myb, MBS1 (p<0.001***/+++), MBS2 (p<0.05*/+), and MBS4 (p<0.001***/+++) were relevant to transcriptional activity when compared to promoter, regardless of c-Myb expression (n = 12). Co-transfection with exogenous c-Myb is however, associated with increased transcriptional activity (p<0.05, n = 3). (D) The human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line (CNE2) is known to express c-Myb. Intact MBS1 (p<0.05*) and MBS4 (p<0.05*, n = 3) were also necessary for miR-143/145 promoter activity in this cell line.