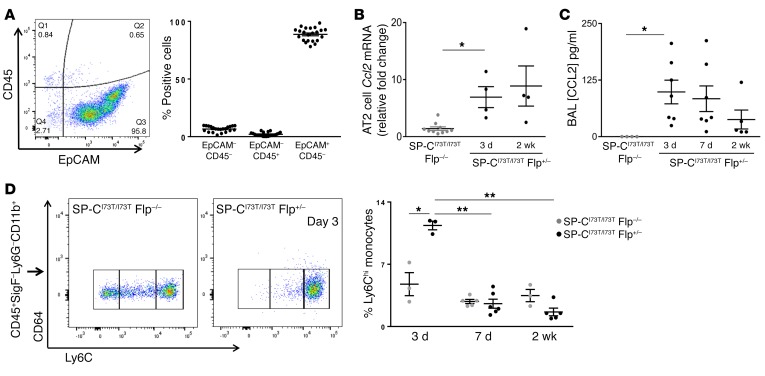
Figure 8. Ccl2 mRNA expression by SftpcI73T AT2 cells precedes BALF CCL2 and recruitment of Ly6ChiCD64– monocytes in lung tissue.
(A) Flow cytometry analysis for EpCAM (CD326) and CD45 expression in AT2 cells isolated from IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp–/– and IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp+/– mice. Dot plot showing EpCAM+CD45– (epithelial), EpCAM–CD45+ (immune), and double-negative populations as a percentage of total cells from each preparation (n = 22 animals). (B) qRT-PCR of AT2 RNA for Ccl2 expression (18S-normalized) for IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp+/– group expressed as fold change (black dots) over IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp–/– controls pooled from both time points (gray dots). *P < 0.05 versus using 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. (C) CCL2 (MCP-1) ELISA of BALF from IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp–/– and IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp+/– cohorts. Dot plots with mean ± SEM are shown. Controls were pooled from IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp–/– at all 3 time points (all less than detectable limit). *P < 0.05 versus control group using 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. (D) Representative flow cytometry plot of lung cell suspensions for CD45+Ly6ChiCD64– populations in IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp–/– and IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp+/– mice on day 3. Dot plot (3 mice pooled per data point) with mean ± SEM showing relative percentage of Ly6ChiCD11c–CD64–CD11b+CD24–Ly6G– monocytes. Multiple comparisons were made by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. For Ly6Chi populations, *P < 0.05 for IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp+/– versus day 3 IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp–/–; **P < 0.05 for 3 day IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp+/– group versus IER-SP-CI73T/I73TFlp+/– at 7 or 14 days.