Fig. 4.
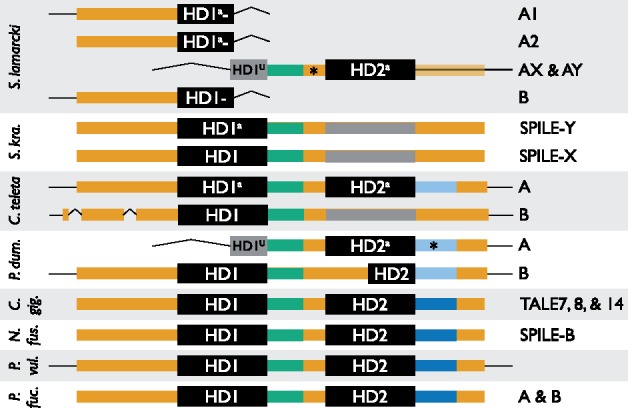
—A schematic of the sequence fragments of TALE clade IV (TALE-IV) family genes, showing the evidence for genes containing two TALE-class HDs. Noncoding sequence is indicated with a thin black line. Coding sequence is indicated with a thick colored line; semitransparent if the extent of the exonic sequence is not easily predictable. Green and blue regions represent areas of high sequence conservation C-terminal to each of the homeodomains. Light blue coloration represents regions where the sequence is recognisably homologous to the blue region but has substantially diverged. Regions that are unusually long relative to equivalent homologous regions are marked with an asterisk. Regions with apparent homology to homeodomains but which have degraded are represented with thick grey lines. Homeodomains are represented with boxes colored black if recognized by the NCBI Conserved Domain Search or grey otherwise. Half-size homeodomains are due to introns (S. lamarcki AX and AY, P. dumerilii A) or truncated homeoboxes (P. dumerilii B). Homeodomains are marked “a” if they belong to the A/annelid-only subclade (see fig. 3) or “U” if they were too short to be identified using the phylogeny. Where two or more paralogues have structures equivalent for the purposes of this diagram, they have been amalgamated and listed to the right. Not to scale. Annelid species: S. lamarcki, Spirobranchus lamarcki; S. kraussi, Spirobranchus kraussi (formerly Pomatoleios); C. teleta, Capitella teleta; P.dum., Platynereis dumerilii. Mollusc species: C. gig., Crassostrea gigas; P. fuc., Pinctada fucata; N. fus., Nipponacmea fuscoviridis; P. vul., Patella vulgata.
