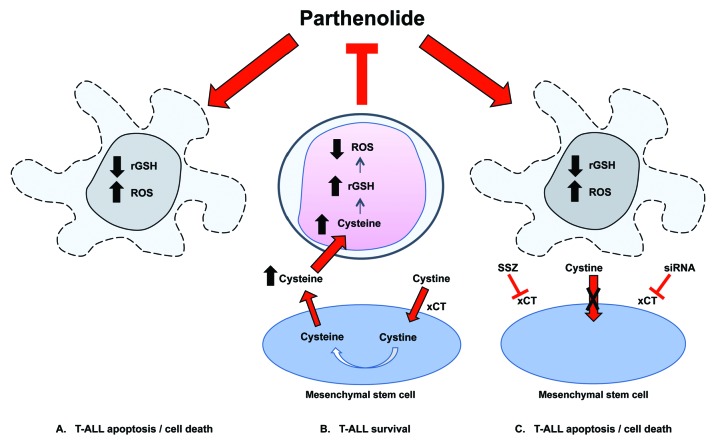
Figure 6.
Proposed mechanism of action of parthenolide (PTL) and the protective effect provided by mesenchymal stem cells (MSC). PTL causes apoptosis by increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS) stress and decreasing reduced glutathione (rGSH) resulting in death of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) cells (A). MSC express high levels of the cystine glutamate antiporter xc-, facilitated by the antiporter protein xCT. Extracellular cystine is taken up by MSC and reduced into cysteine. Cysteine is released into the extracellular space for uptake by T-ALL cells, blocking ROS induction and preventing apoptosis (B). Blocking the xCT system using sulfasalazine (SSZ) or siRNA reduces protective effects provided by MSC(C).