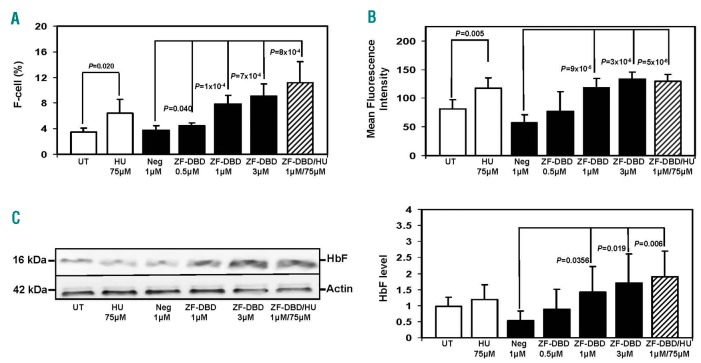
Figure 2.
Increased number of F-cells and fetal hemoglobin (HbF) production in sickle erythroid progenitors treated with the -567GγZF-DBD. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were induced to differentiate toward erythroid progenitors and exposed to hydroxyurea (HU), -567GγZF-DBD (ZF-DBD), or NC-ZF-DBD (Neg) as described in the legend to Figure 1. (A) Cells were stained with FITC labeled anti-γ-globin antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry. Shown is the number of HbF positive cells (F-cells) after treatment with the various agents. Graphical quantification of F-cell counts from 3 independent experiments analyzed in triplicate (n=9), with error bars reflecting the Standard Deviation (SD). (B) Graphical representation of the mean fluorescence intensity of cells described in (A) from 3 independent experiments. (C) Analysis of protein expression in erythroid progenitors treated under the different conditions shown. Western blot analysis was performed with antibodies specific for human HbF and b-actin. (Left) Representative western blot. (Right) Densitometry data from 3 independent western blot experiments performed in triplicate (n=9); error bars represent SD.