Figure 4.
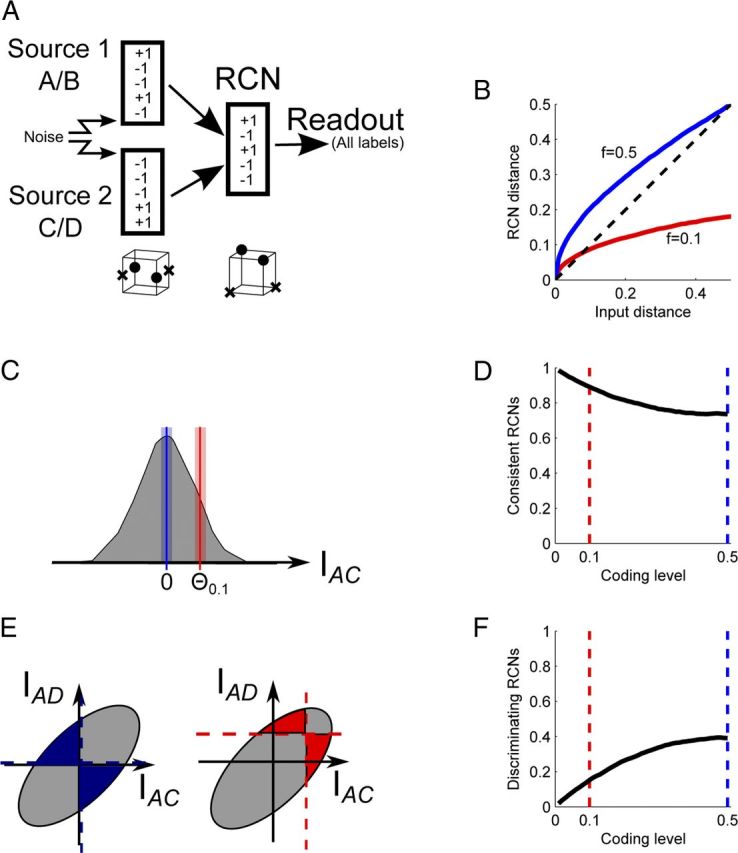
RCN coding level shifts the balance between discrimination and generalization. A, Neural architecture, as in Figure 1C. The crosses and circles represent the patterns to be classified, as in Figure 1D. The original segregated representations are nonlinearly separable for a classification problem analogous to the exclusive OR (opposite points should produce the same output). The RCNs increase the dimensionality, making the problem linearly separable (now a plane can separate crosses from circles). B, Transformation of Hamming distances in the RCN space for two coding levels (blue, 0.5; red, 0.1). The distance in the RCN space is plotted versus the distance in the input space. Although distances are distorted, their ranking is preserved (e.g., small distances map to small distances). C–F, How generalization and discrimination abilities vary with the coding level of RCN representations. C, The generalization ability is estimated as the fraction of RCNs that respond in a consistent manner to noisy realizations of the same input (n = 0.1). The shaded area represents the distribution of input currents to different RCNs for a particular input pattern (A, C, for the two sources, respectively). For dense representations (blue, threshold at zero) there is a larger fraction of RCNs that is around the activation threshold compared to the sparse case. D, The fraction of consistent RCNs decreases with coding level. E, The discrimination ability is estimated as the fraction of RCNs that respond differentially to a pair of patterns, differing only by the state of one source. The gray area represents the distribution of the currents to the RCNs for AC and AD inputs (differing in the second source). The area of colored shading represents the fraction of RCNs that respond differentially to the two combinations of inputs (for one input the current is positive and for the other it is negative). F, Discrimination increases with coding level.
