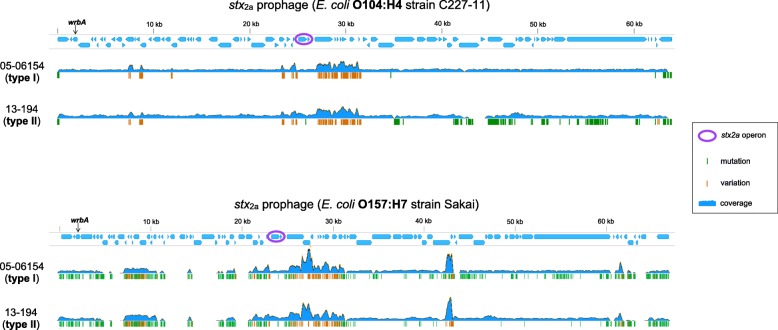
Fig. 4.
Different stx2a-converting prophages in EHEC O26 nEC strains. Visualization of sequencing reads mapped onto stx2a-converting prophages from E. coli O104:H4 strain C227–11 (GenBank accession: CP011331; top) and E. coli O157:H7 strain Sakai (GenBank accession: NC_002695; bottom). Strains 05–06154 and 13–194 represent the two distinct patterns of stx2a-converting prophages (type I and type II, respectively), which were detected among EHEC O26 nEC strains (see Fig. 2). Green vertical lines represent true mutations with respect to reference sequence. Orange vertical lines represent hybrid positions containing variant bases, which coincide with regions of abnormally high sequencing coverage (plausibly representing contributions of sequencing reads from other lambdoid prophages [68])