Figure 1.
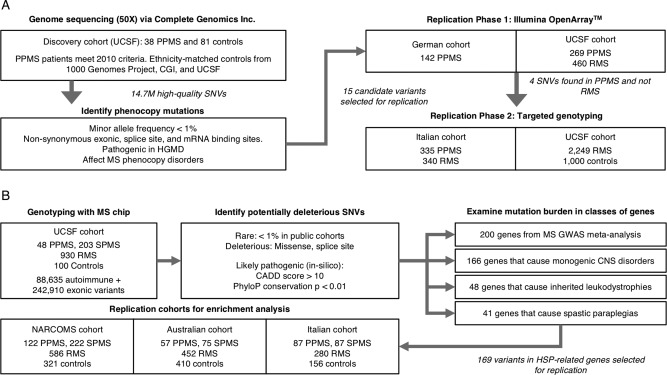
Summary of study cohorts, genotyping platforms, and variant selection. (A) Schematic of study design used for identifying MS phenocopy variants. The WGS discovery cohort included 38 PPMS patients (who met 2010 International Panel Criteria) and 81 ethnicity‐matched controls sequenced using the Complete Genomics Inc. (CGI) platform. Fifteen candidate variants were selected for Phase 1 replication genotyping in 411 PPMS and 460 RMS patients using OpenArray. Four top candidate variants exclusively found in PPMS and not RMS patients were selected for Phase 2 replication in 335 PPMS and 340 RMS patients from an Italian cohort and in 2,249 RMS and 1,000 controls from UCSF. (B) Schematic of study design used for determining the burden of HSP‐related mutations in PPMS. The discovery cohort comprised of 48 PPMS patients (who met 2010 International Panel Criteria) and 100 controls genotyped on the MS replication chip. Replication patients included an additional 266 PPMS, 1,702 RMS, and 887 control subjects from three additional cohorts (NARCOMS, Australian, and Italian) genotyped on the same platform. All subjects examined were of European ancestry. CADD = Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion; CNS = central nervous system; GWAS = genome‐wide association studies; HGMD = Human Gene Mutation Database; HSP = hereditary spastic paraplegia; MS = multiple sclerosis; NARCOMS = North America Research Committee on Multiple Sclerosis; PhyloP = phylogenetic conservation p value; PPMS = primary progressive multiple sclerosis; RMS = relapsing multiple sclerosis; SNVs = single‐nucleotide variants; SPMS = secondary progressive multiple sclerosis; UCSF = University of California San Francisco; WGS = whole‐genome sequencing.
