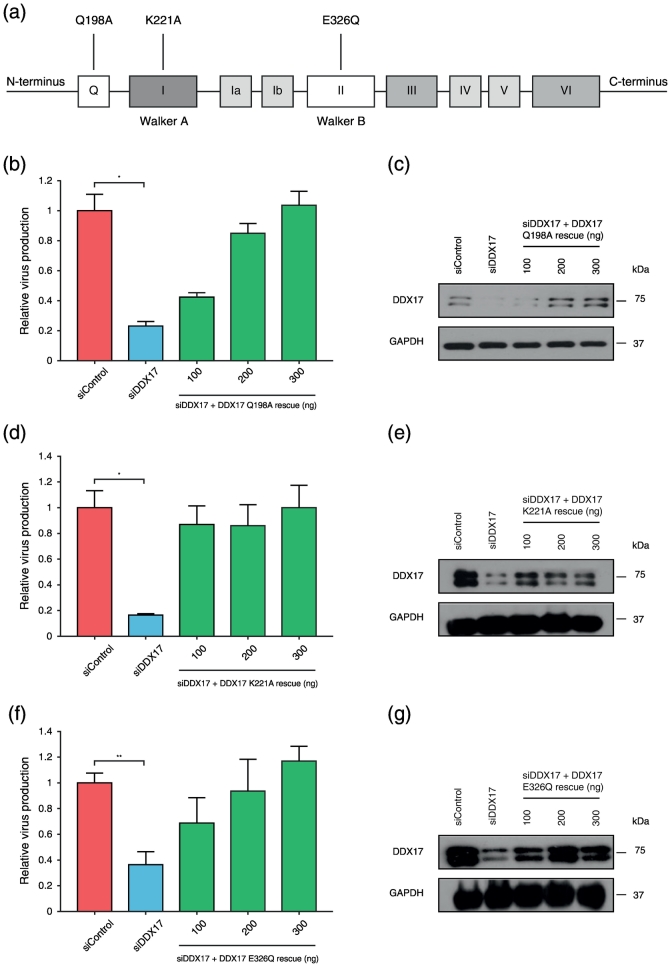
Fig. 6.
DDX17 Q, Walker A and Walker B motifs are dispensable in HIV-1 replication. (a) Schematic representation of DDX17 and the annotated individual point mutations in the Q motif that abrogates ATP binding and hydrolysis, and in the Walker A and Walker B (DEAD) motifs that are defective for ATPase and helicase activity, respectively. HeLa M cells were sequentially transfected with siControl or siRNA targeting DDX17 (siDDX17 with or without increasing concentrations of siDDX17-resistant DDX17–Q198A or siDDX17-resistant DDX17–K221A or siDDX17-resistant DDX17–E326Q). (b) Effect on HIV-1 relative virus production following endogenous DDX17 knockdown and rescue with DDX17–Q198A. (c) Western blot showing DDX17 knockdown and rescue with DDX17–Q198A. (d) Effect on HIV-1 relative virus production following endogenous DDX17 knockdown and rescue with silent Walker A (DDX17–K221A). (e) Western blot showing DDX17 knockdown and rescue with DDX17–K221A. (f) Effect on HIV-1 relative virus production following endogenous DDX17 knockdown and rescue with silent Walker B (DDX17–E326Q). (g) Western blot showing DDX17 knockdown and rescue with DDX17–E326Q. Each graph is a representative of three independent experiments done in triplicate ± SEM. Statistical significance: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.