Figure 2.
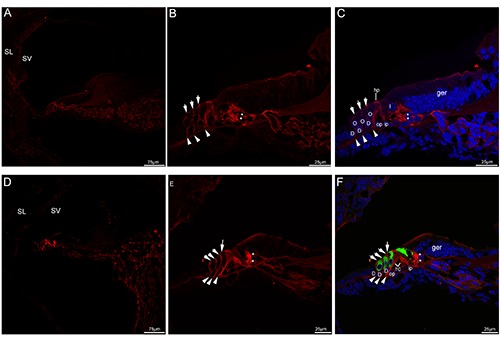
Acetylated tubulin immunolabeling in the mouse cochlea at P5 and P8. A) An overview of acetylated tubulin (red) labeling in the medial turn of the mouse cochlea at P5. B,C) Detail of acetylated tubulin (red) labeling in the organ of Corti in the medial turn of P5. The neural plexus (asterisks) beneath the inner hair cell showed acetylated tubulin immunolabeling, three discrete rows of fibers (arrowheads) under the outer hair cell stained positively for acetylated tubulin. Note that the phalangeal processes (small arrows) of premature Deiters’ cells that lied between outer hair cells began to express acetylated tubulin, moderate immunolabeling was seen in the head plates of the pillar cells. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). D) An overview of acetylated tubulin (red) labeling in the medial turn of the mouse cochlea at P8. Acetylated tubulin (red) labeling seemed to be limited to the organ of Corti. E,F) Detail of acetylated tubulin (red) labeling and myosin VIIa (green) labeling in the organ of Corti in the medial turn of P8 and the merged image +DAPI. The tunnel of Corti opened up between most of the lower portions of inner and outer pillar cells, acetylated tubulinlabeled nerve terminals (asterisks) became more clustered around the base of the inner hair cells, acetylated tubulin (red) labeling was also observed three discrete rows of fibers (arrowheads) under the outer hair cell. Acetylated tubulin-labeled the phalangeal processes of Deiters’ cells (small arrows) filled the spaces between the outer hair cells. Noted that a process (large arrow) was extended by the inner pillar cell and expressed acetylated tubulin. D, Deiters’ cell; I, inner hair cell; O, outer hair cell; TC, tunnel of Corti; ger, greater epithelial ridge; hp, head plate; op, outer pillar cell; ip, inner pillar cell; SL, spiral ligament; SV, stria vascularis.
