FIGURE 2.
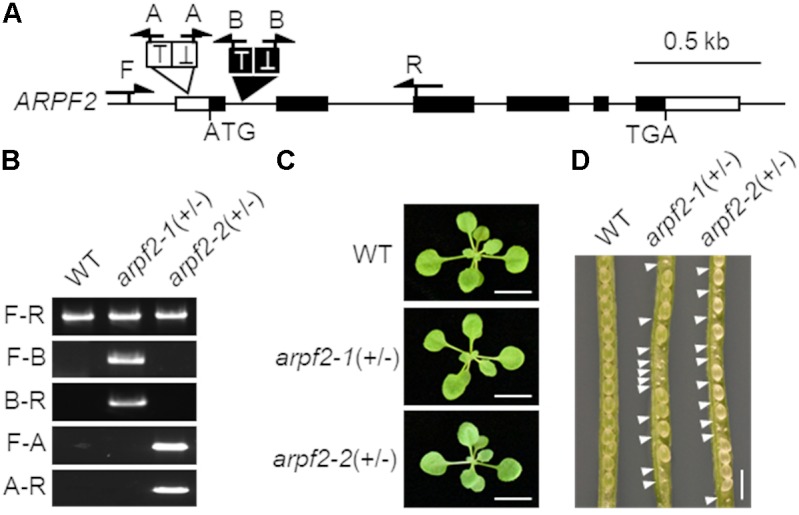
arpf2 mutations lead to embryonic lethality in Arabidopsis. (A) Schematic representation of the ARPF2 locus. White and black boxes indicate untranslated and coding regions in the exons of ARPF2, respectively. Black and white triangles indicate the positions of tandem T-DNA insertions in the arpf2-1 and arpf2-2 mutant alleles, respectively. Arrows indicate the positions of primers used for genotyping in (B). (B) PCR-based genotyping. Wild type (WT) and heterozygotes for the arpf2-1 or arpf2-2 allele [arpf2-1(+/–) and arpf2-2(+/–)] were analyzed using primers (F, R, A, and B) indicated in (A). Sets of primers F and R (F-R), primers F and A (F-A), primers A and R (A-R), primers F and B (F-B), and primers B and R (B-R) were applied. (C) Photographs of 2-week old plants grown on agar plates. Scale bars: 1 cm. (D) Photograph of seeds in fruits. White arrowheads indicate the aborted embryos. Scale bar: 1 mm.
