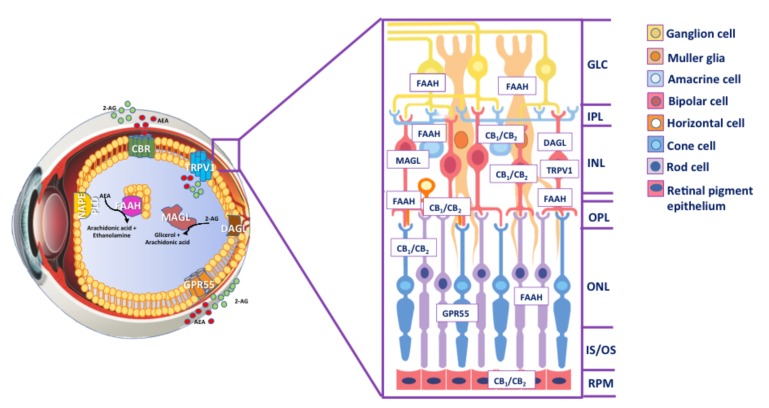
Fig. (1).
Inside the eye. Schematic representation of the human eye with an overview of ECS distribution. AEA is manly synthesized by NAPE-PLD, whereas DAGL is the most important enzyme for the biosynthesis of 2-AG. AEA and 2-AG signalling pathways are terminated by enzymatic hydrolysis, mediated primarily by the serine hydrolases FAAH and MAGL, respectively. In the cross-section, the presence of ECS element in different layers of the retina is shown. Abbreviations: AEA, anandamide; 2-AG, 2-arachidonoylglycerol; NAPE-PLD, N-arachidonoylphosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase D; DAGL, diacylglycerol lipase; FAAH; fatty acid amide hydrolase; MAGL, monoacylglycerol lipase; CBR, cannabinoid receptors; GPR55, G protein-coupled receptor 55; TRPV1, transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1; GLC, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; IS/OS photoreceptor layer; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium.