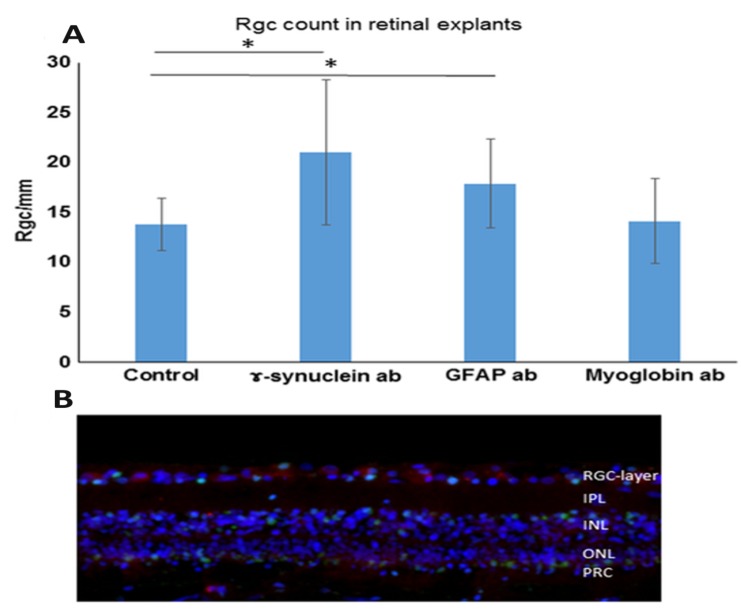
Fig. (1).
Effect of abs on the number of RGCs. Retinal explants were cultivated with control medium without additional abs (control retinae) or with medium with additional 0.5 μg/mL γ-Synuclein abs or 1 μg/mL glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) abs for 24 h. Furthermore, retinal explants were also incubated with medium with added anti-myoglobin abs serving as an isotype-matched control ab (0.5 μg/mL anti-myoglobin abs). The retinae were fixed, embedded and then prepared for immunohistological staining. The cells were counted manually and quantified using ImageJ and subsequent statistics were performed. *p < 0.05 (error bars are standard deviation). (A) Quantification of RGC/mm: We were able to detect significantly increased RGC numbers in both the retinae incubated with GFAP abs as well as retinae incubated with γ-Synuclein abs. The RGC number in GFAP ab-treated retinal explants was 20.1 RGC/mm. The RGC number in γ-Synuclein ab-treated retinal explants: 20.8 RGC/mm. The control retinae counted up to 13.8 RGC/mm and the retinae incubated with the control antibody (anti-myoglobin antibody) showed 14.15 RGC/mm. (B) Example image of retinal explant incubated with γ-Synuclein abs for 24 h. Immunohistological staining was performed in which the nuclei are shown in blue (DAPI staining), the RGC in red (Brn3a staining) and apoptotic cells in green (TUNEL staining) (modified after: [76], published in Bell, K.; Wilding, C.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of antibodies on retinal ganglion cells in an adolescent retina organ culture. J Neurochem, 2016, 139(2), 256-269./permission number: 4081430398238).