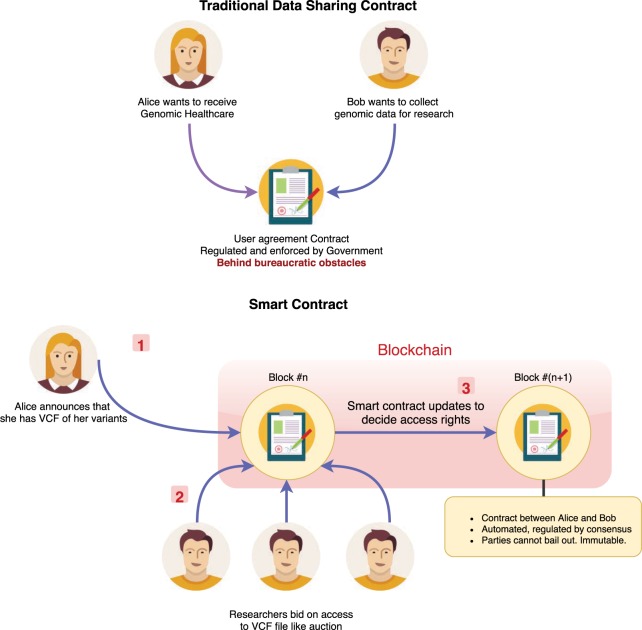
Figure 1.
A smart contract to manage access management for genomic data. In traditional agreements, both parties sign a contract that dictates the boundaries, which the participants must obey. A third party is often required to enforce the agreement conditions. Smart contracts, on the other hand, can eliminate the need for a third party. In this figure, Alice publishes an encrypted version of her VCF file. At first, no other participant or researcher can analyze this file. In the second round, smart contract accepts bidding transactions for this file. The highest bidder is then selected to be the rightful owner and gets access to the file through an algorithmic process.