Figure 1. Rtt105 binds RPA in vivo and in vitro .
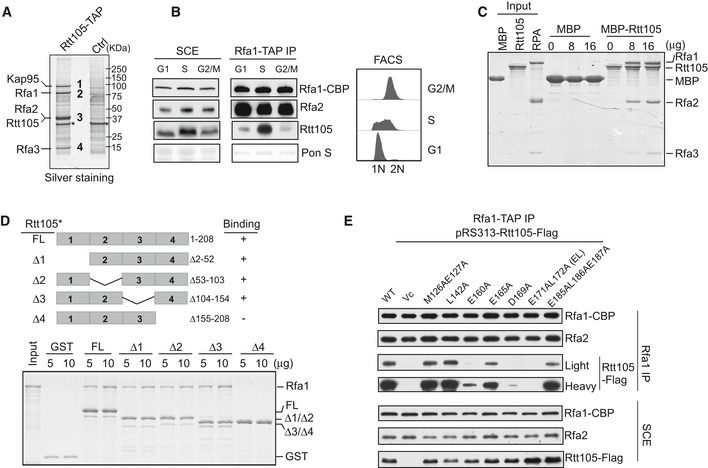
- Identification of Rtt105‐TAP‐associated proteins. Purified proteins were resolved on a 4–12% gel, revealed by silver staining, and identified by mass spectrometry (Table EV1). Asterisk (*) indicates non‐specific band also in control.
- Cells containing Rfa1‐TAP were synchronized at G1, S, and G2/M phases and used for the TAP purification. Rfa1‐TAP‐associated protein complexes were analyzed by Western blot using CBP, Rfa2, and Rtt105 antibodies (left panel). DNA content was monitored by flow cytometry (right panel).
- MBP‐Rtt105 pulled down recombinant RPA, resolved on SDS–PAGE gels and visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining. MBP was used as a negative control.
- GST‐tagged full‐length (FL) and Rtt105 deletion mutants (schematic of the Rtt105 truncations is shown in the upper panel) were purified and used to pull down Rfa1 protein. GST proteins were used as a negative control. Isolated protein complexes were resolved on 15% SDS–PAGE gels and visualized by CBB staining.
- Rfa1‐TAP purification was performed using Rfa1‐TAP rtt105Δ strains expressing WT and indicated Rtt105 mutant forms. pRS313 serves as vector control (Vc).
Source data are available online for this figure.
