-
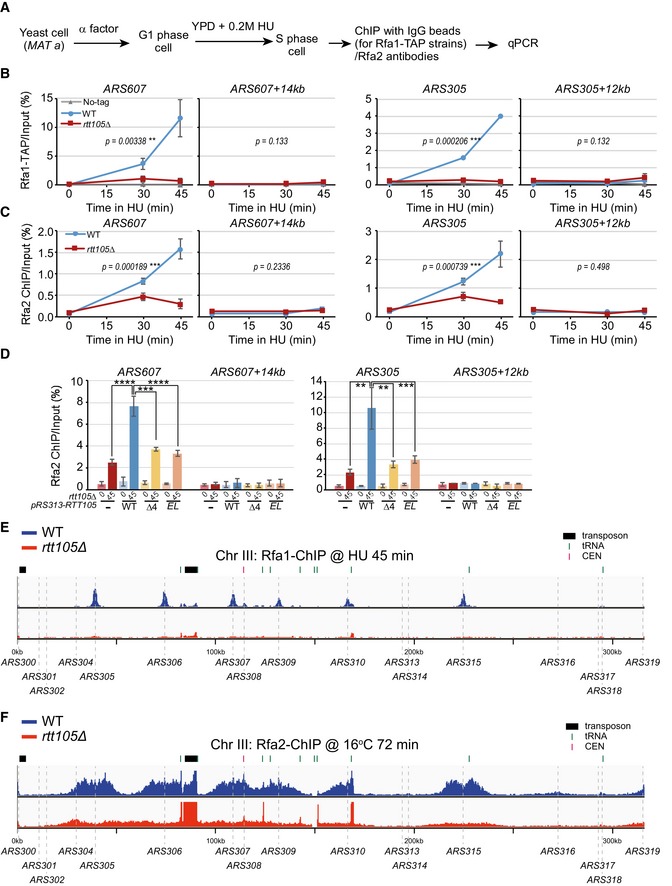
A
An outline for ChIP assays for Rfa1 and Rfa2 subunits. G1 yeast cells were released into fresh YPD medium containing 0.2 M HU to arrest cells at early S phase. Equal amounts of cells were collected prior to G1 (0 min) or at different time points following release. Rfa1 and Rfa2 ChIP was performed using IgG beads for TAP‐tagged strains, or anti‐Rfa2 antibody.
-
B, C
RPA binding was dramatically decreased at HU‐stalled replication forks upon deletion of RTT105. ChIP DNA and input DNA were analyzed by quantitative real‐time PCR using primers against the replication origins ARS607 and ARS305 and their corresponding distal regions (ARS607 + 14 kb and ARS305 + 12 kb), and the percentage of ChIP DNA over the input DNA was calculated. The mean and standard error (SE) of at least two biological replicates are shown, with P‐values derived from two‐way analysis of variance (ANOVA; **0.001 ≤ P‐value < 0.01, ***P‐value ≤ 0.001).
-
D
The C‐terminus of Rtt105 is important for RPA binding at replication forks. pRS313‐based plasmids expressing Flag‐tagged WT Rtt105 and mutants (Δ4 and EL) were transformed into the rtt105Δ strain. ChIP was performed using Rfa2 antibodies. Vc: pRS313 vector; WT: pRS313‐Rtt105‐Flag; Δ4: pRS313‐Rtt105 (Δ155–208)‐Flag; EL: pRS313‐Rtt105E171AL172A‐Flag. The mean and standard error (SE) of two biological replicates are shown. Statistical significance was evaluated based on Student's t‐tests (**0.001 ≤ P‐value < 0.01, ***0.0001 ≤ P‐value < 0.001; ****P‐value < 0.0001).
-
E
Snapshot of Rfa1 ChIP‐seq at chromosome III under HU synchronized cells is shown. Yeast cells were synchronized at G1 phase and then released into fresh medium containing 0.2 M HU and 400 μg/ml BrdU for 45 min at 25°C. Equal amounts of cells were collected just prior to G1 (0 min) or at 45 min following release into early S phase in the presence of HU. Rfa1 ChIP DNA was processed for sequencing. The sequencing reads were mapped to the yeast reference genome.
-
F
Snapshot of Rfa2 ChIP‐seq at chromosome III at S phase without HU treatment is shown. G1‐arrested yeast cells were released into S phase at low temperature (16°C) without HU. Yeast cells were collected for Rfa2 ChIP and were further processed for sequencing. The sequencing reads were mapped to the yeast reference genome.