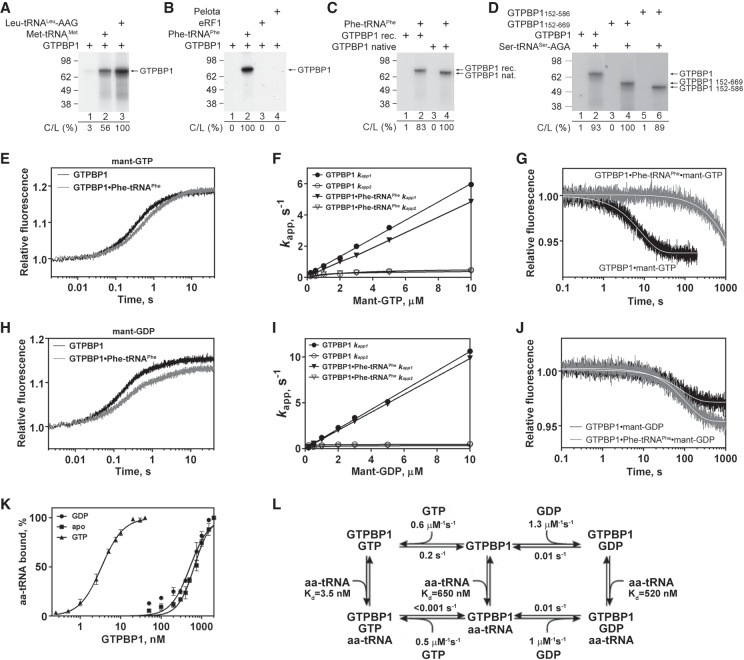
Figure 2.
Interaction of GTPBP1 with guanine nucleotides. (A–D) UV cross-linking of different forms of GTPBP1 to [α-32P]GTP depending on the presence of aa-tRNAs, Pelota, and eRF1, as indicated. Cross-linked proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. The efficiency of cross-linking (C/L) was quantified by phosphorimager and normalized to the condition with the highest cross-linking. (E–J) Binding kinetics of methylanthraniloyl GTP (mant-GTP) and mant-GDP to GTPBP1, monitored by stopped-flow. (E,H) Time courses of the association of 5 µM mant-GTP (E) and 5 µM mant-GDP (H) with 50 nM GTPBP1 in the absence or presence of 150 nM Phe-tRNAPhe. (F,I) Concentration dependence of apparent rates kapp1 and kapp2 of mant-GTP (F) and mant-GDP (I) binding to GTPBP1 in the absence or presence of Phe-tRNAPhe. (G,J) Time courses of the dissociation of mant-GTP (G) or mant-GDP (J) from GTPBP1 alone or in the presence of Phe-tRNAPhe upon chase with 500 µM GTP or 500 µM GDP, respectively. (K) Association of GTPBP1 with [35S]Cys-tRNACys depending on the presence of guanine nucleotides, assayed by filter binding. (L) Kinetic scheme of the interaction of GTPBP1 with guanine nucleotides and aa-tRNA.