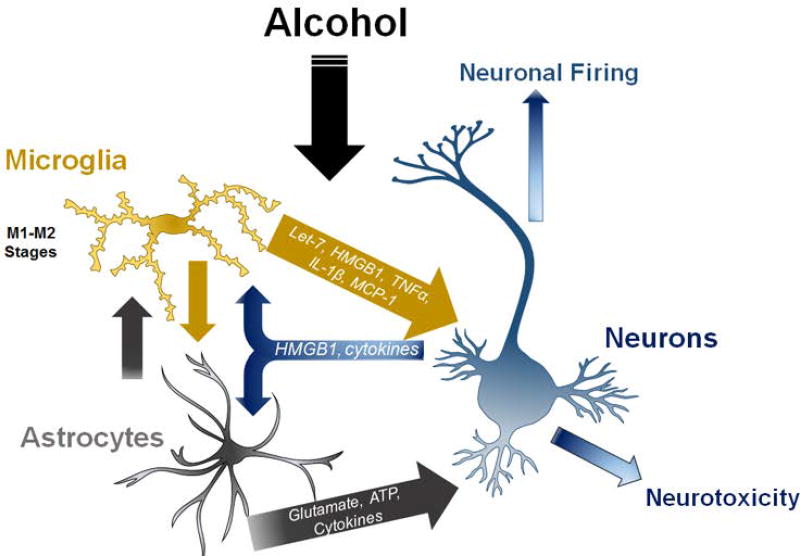
Figure 5. Neuron-glia cell-cell interactions in neuroimmune responses to alcohol.
Neuronalglial interactions underlie neuroimmune signaling in alcohol use disorders. Microglia release factors such as microRNA let-7, HMGB1 and cytokines that can cause either neurotoxicity or altered neuronal activity. Microglia and astrocytes likely release factors that alter each other’s activation status. Astrocytes modulate glutamate and ATP levels that affect neuronal signaling and vitality. Neurons release factors such as HMGB1, fractalkine and cytokines that can modulate microglial and astrocyte activation. See References: [19, 21, 27, 74, 77, 157]