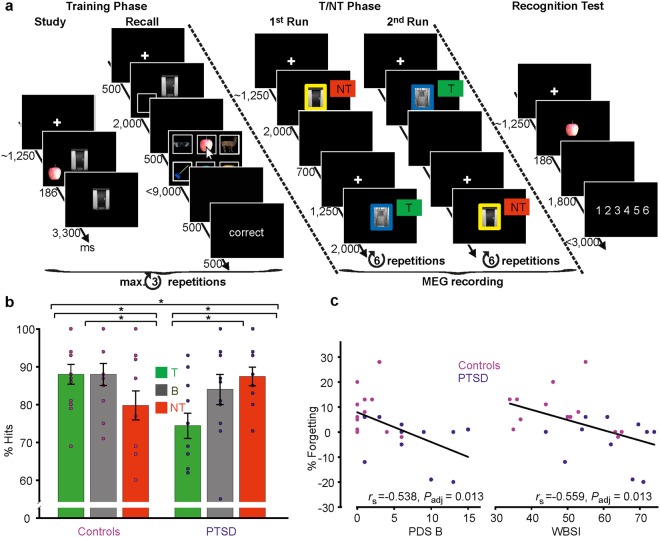
Figure 1.
Experimental procedure and behavioral results. The T/NT task (a) consisted of three phases: Training, T/NT and recognition test phase. In the think condition (‘T’), participants were instructed to practice retrieval of everyday objects when being presented with a visual cue associated to the object during the training phase. In the no-think condition (‘NT’), participants were instructed to directly suppress the associated target object and to avoid any thought about it, without retrieving or focusing on alternative memories or thoughts. Memory performance in a subsequent surprise recognition test for T and NT items was compared to recognition performance for baseline (‘B’) items that were initially studied, but did not occur in the T/NT phase. (b) Item recognition memory performance showing a significant (P < 0.05) Group × Condition interaction and significant post-hoc comparisons as indicated by asterisks. Bars represent mean hit rates together with ±1 standard error of the mean and individual data points. See main text for statistical details. (c) Significant Spearman-rank correlations between suppression-induced forgetting and clinical measures of re-experiencing symptoms (PDS B) and thought suppression in everyday life (WBSI).