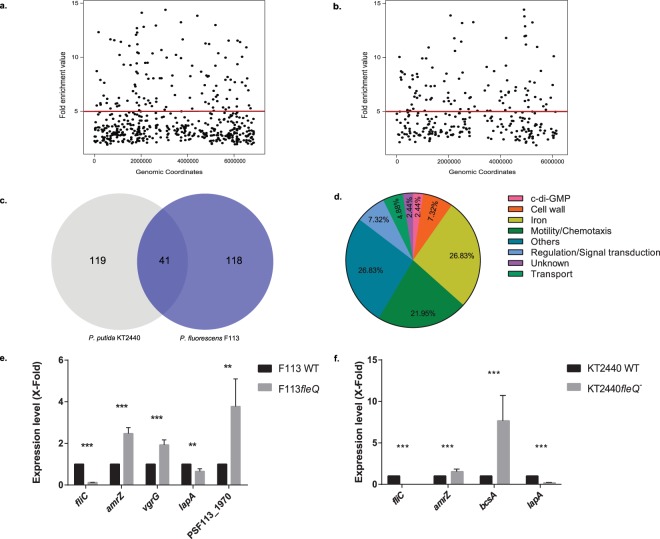
Figure 2.
FleQ is a global transcriptional regulator that can act both as an activator and as repressor in P. fluorescens F113 and P. putida KT2440. FleQ binding sites distribution along the P. fluorescens F113 (a) and P. putida KT2440 genomes (b). Fold enrichment value for each of the peaks after peak calling with MACS 1.4 is represented against the coordinates in which these accumulations are located. Red line marks the five-fold enrichment threshold fixed in the analysis. Venn diagram representation of the genes predicted to be in FleQF113 and FleQKT2440 regulons (c). Pie chart depicting the functional classification of FleQ-regulated genes shared by P. fluorescens F113 and P. putida KT2440. Percentage of the 41 genes shared by both species in each functional category according to Gene Ontology database is represented (d). Genes included in these graphs are listed in Table 1. Gene expression analysis of putative FleQ-regulated genes by RT-qPCR assays in P. fluorescens F113 (e) and P. putida KT2440 (f). Expression level in the wild-type strain was considered 1 for each of the tested genes. Fold variation for each gene was determined by the 2−ΔΔCT method. RNA was extracted after growth in SA medium to an O.D.600 ≈ 0.8. The asterisks denote statistically significant differences (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001) found with t-test for independent samples and Bonferroni-Dune method.