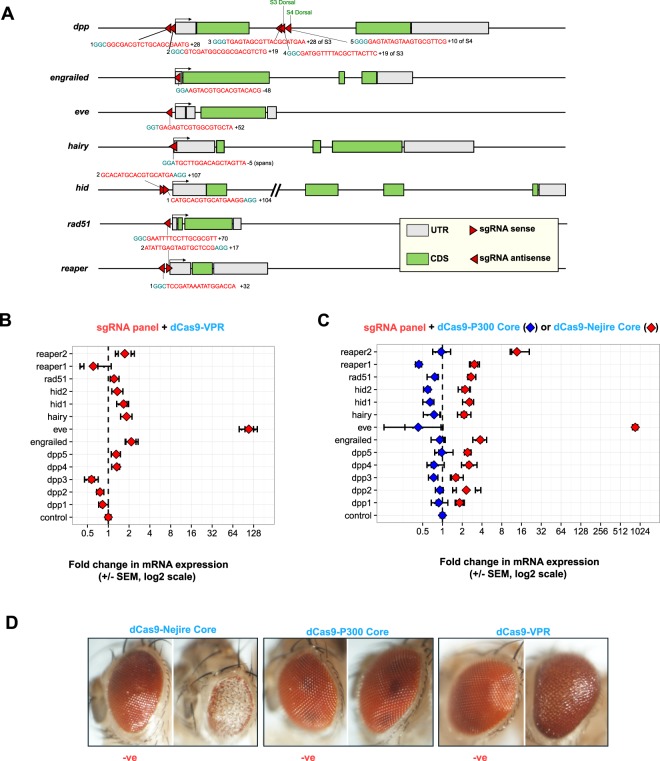
Figure 2.
Design and testing of sgRNAs and dCas9 activators. (A) Gene architecture of 7 developmental target genes showing the position and orientation of the sgRNA binding sites and sequence (red) and the Protospacer Adjacent Motif (PAM, blue). Numbers flanking the target sequence indicate the sgRNA-strain. TSS indicated by 90° arrow. Base pair distance to the TSS is indicated (+upstream, -downstream). For dpp additional sgRNAs 3, 4 and 5 were designed to target close to S3 and S4 Dorsal binding sites (green). The hid intron 1 has been truncated (slashed lines). (B) qRT-PCR analysis of target gene expression levels when the sgRNA panel was tested in a UAS::dCas9-VPR/GMR-GAL4 genetic background (Supplementary Technical Cross 1 A). The control indicates eve expression in the absence of sgRNA. Two biological replicates were measured for each condition with the mean shown in red. Error bars show 95% confidence limits, calculated from three technical replicates. (C) Testing of transactivation potential of Histone Acetyltransferase domain dCas9 fusions in eyes (Supplementary Technical Crosses 1B and 1 C). qRT-PCR analysis of target gene expression levels in the head using dCas9-P300 Core (mean of 2 biological replicates shown as blue diamonds) and dCas9-Nejire Core (mean of two biological replicates shown as red diamonds) under GMR-GAL4 control in eyes and sgRNAs. The control indicates eve expression in the absence of sgRNA. Error bars as in B. (D) Exemplary eye phenotypes of dCas9 activator fusions expressed from GMR-GAL4 in absence or presence of eve-sgRNA. A severe, aberrant phenotype is seen with eve-sgRNA and dCas9-Nejire Core. Moderate developmental eye phenotypes are seen with dCas9-Nejire Core in the absence of sgRNA and when dCas9-VPR is in complex with eve-sgRNA.