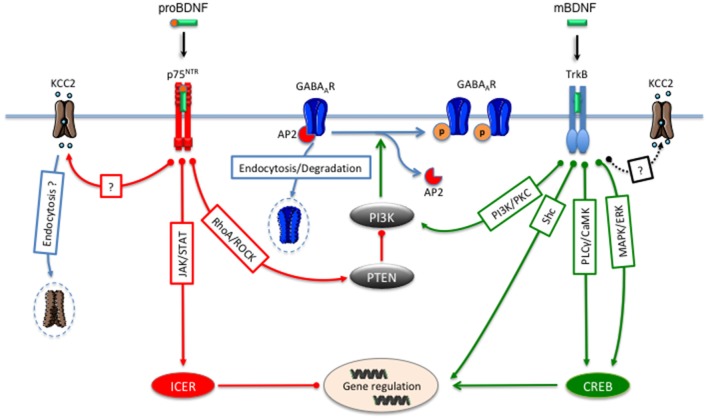
Figure 1.
mBDNF/TrkB and proBDNF/p75NTR signaling pathways regulate γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmission. Activation of TrkB receptors by mBDNF leads to an inhibition of GABAAR endocytosis and a consequent increase in the cell surface expression of these receptors through the PI 3-kinase and the PKC signaling pathway. At the transcriptional level, BDNF/TrkB signaling regulates GABAAR and KCC2 gene expression through the Shc, PLC/CaMK or MAP/ERK pathways. Activation of p75NTR by proBDNF decreases GABAARs cell surface expression through the RhoA/ROCK/PTEN pathway that leads to the dephosphorylation of GABAAR and endocytosis and degradation of internalized receptors. At the transcriptional level, proBNDF/P75NTR leads to the repression of GABAAR synthesis through the JAK2/STAT3/ICER pathway. The proBDNF/75NTR signaling also decreases KCC2 expression.